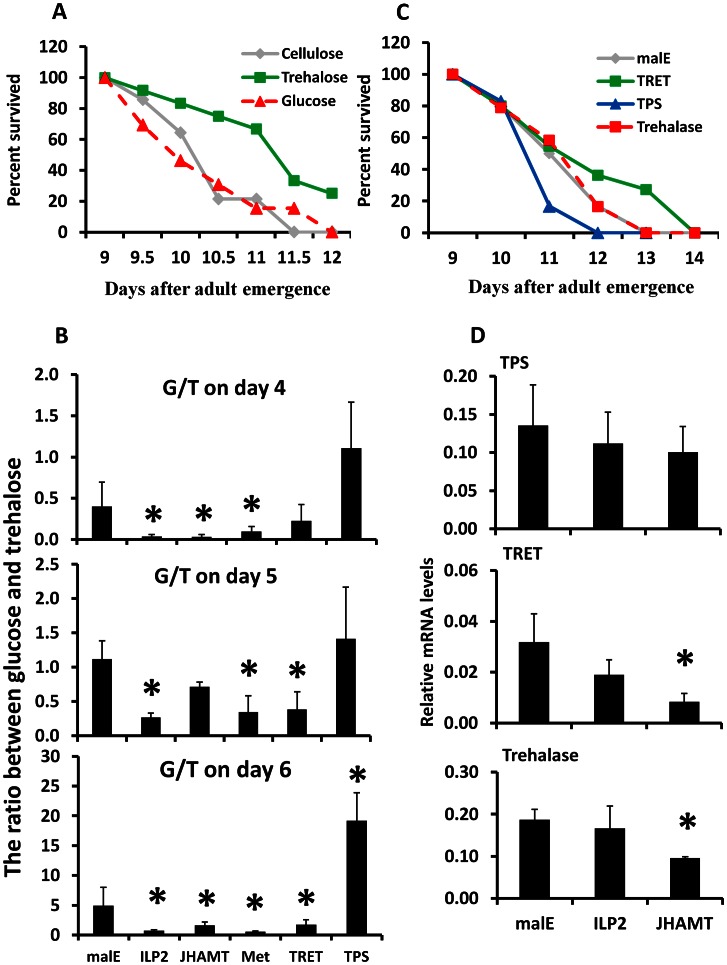
Figure 3. Trehalose metabolism plays an important role in extending life span during starvation.
A. Starvation survival after feeding 10% trehalose plus cellulose, 10% glucose plus cellulose, or cellulose alone to the 8-day-old starved male beetles. The survival was recorded from day 9 to day 12. B. The ratio between hemolymph glucose and trehalose on days 4, 5, and 6 after injection of malE, ILP2, JHAMT, Met, TRET, or TPS dsRNA into the newly emerged adults. The hemolymph was extracted from three beetles for each treatment. The trehalose concentrations were determined using the glucose reagent and trehalase. The data shown are the Mean+S.D. (n = 6). C. Starvation survival after manipulation of endogenous trehalose level by injecting TRET, TPS, or trehalase dsRNA on day 0. The beetles were starved until 14 days. The survival was recorded from day 9 to day 14. D. The relative mRNA level of TPS, TRET, and trehalase after injecting malE, JHAMT, or ILP2 dsRNA. Total RNA was isolated on day 5 from beetles injected with control malE, JHAMT, or ILP2 dsRNA and starved. The RNA was converted to cDNA, and the relative levels of TPS, TRET, and trehalase mRNA were determined by qRT-PCR using RP49 as a control. The data shown are the Mean+S.D. (n = 3). Asterisks show treatments that are significantly different from the control (P<0.05) in one-way ANOVA.