Figure 2. in vitro-transcription/translation of GP5–HA to assess processing (glycosylation/signal peptide cleavage).
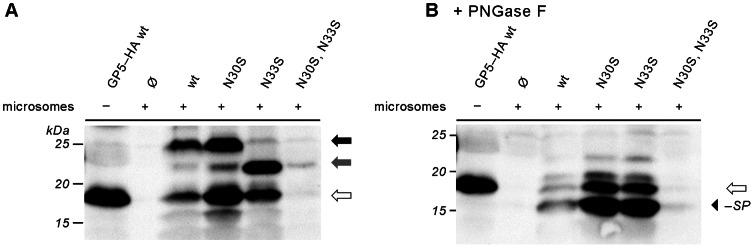
(A), Plasmids encoding GP5–HA was subjected to in vitro-transcription/translation with rabbit reticulocyte lysate in the absence (–) or presence (+) of porcine pancreatic microsomes. The products were analysed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot (anti-HA tag). Wildtype (wt) and mutants with deleted or added glycosylation sites near the signal peptide cleavage site were employed; Ø, empty plasmid control. Molecular weight marker is indicated on the left-hand side, arrows on the right-hand side show the positions of unprocessed GP5–HA (white), fully glycosylated GP5–HA (black), and GP5–HA lacking one glycan (grey). (B), Glycans from the products of (A) were removed with PNGase F prior to SDS-PAGE and Western blot. Deglycosylated protein lacking the signal peptide (black arrowhead) is smaller than unprocessed GP5–HA and deglycosylated protein containing the signal peptide (white arrow), indicating signal peptide cleavage.
