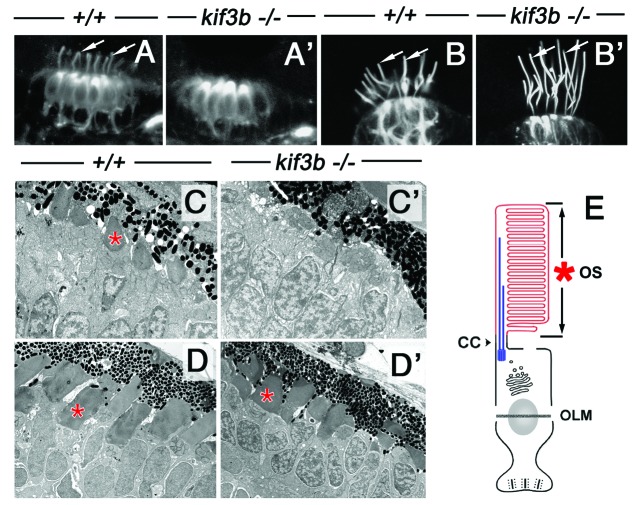
Figure 2. A subset of cilia differentiate in kif3bjj203 mutant embryos. In (A, A’, B and B’), shown are wild-type (A and B) and mutant (A’ and B’) embryos stained with anti-acetylated tubulin antibody at 3 (B and B’) and 7 (A and A’) dpf. (A and A’) Confocal images of a macula in the zebrafish ear. Cilia (arrows) are present in both wild type and mutant. (B and B’) Confocal images of a crista of the zebrafish ear. Cilia (arrows) are absent in the mutant. (C, C’ and D’) Electron micrographs of sections through wild-type (C and D) and mutant (C’ and D’) photoreceptor cells at 3.5 (C and C’) and 5 (D and D’) dpf. Photoreceptor outer segments [OS, asterisks in (C?E)] are initially absent in the mutant. (E) A schematic drawing of the vertebrate photoreceptor cell (after Kennedy and Malicki, 2009). The outer segment membrane is in red. Microtubules that support its structure are in blue. In this work, term “cilium” is used to mean the structure that includes the connecting cilium and the outer segment. The outer segment (OS) forms in the distal part of photoreceptor cilia, which differentiates membrane folds. The connecting cilium (CC), on the other hand, is the proximal region of photoreceptor cilia, and displays characteristics of the ciliary transition zone. OLM, outer limiting membrane.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.