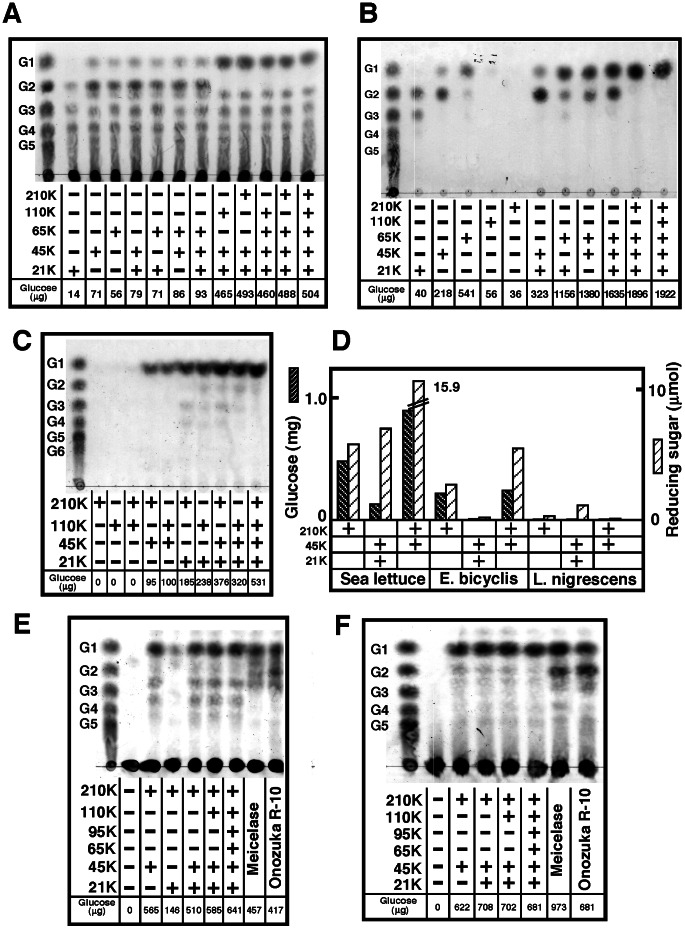
Figure 4. Hydrolysis of CMC, filter paper, and seaweeds by the synergistic action of cellulases and ß-glucosidases.
(A) CMC (1 mL, 1% in 50 mM acetate, pH 5.5) was incubated with various combinations of purified enzymes (2 µg) as indicated at 37°C for 1 h. Reaction products were analyzed by TLC. (B) Filter paper (60 mg) was digested with various combinations of purified enzymes (10 µg) as indicated at 37°C for 48 h, and reaction products were analyzed by TLC. (C) Filter paper (60 mg) was digested with 21 K and 45 K cellulase (2 µg) in the presence of 110 K or 210 K ß-glucosidase (2 µg) at 37°C for 16 h. Reaction products were analyzed by TLC. (D) Seaweed, sea lettuce (Ulva pertusa), Eisenia bicyclis, and Lessonia nigrescens (20 mg in 50 mM acetate, pH 5.5) were incubated with purified enzymes (10 µg) at 37°C for 24 h. Glucose and reducing sugar content were then determined. (E, F) TLC analysis of reaction products of sea lettuce treated with purified enzymes or Trichoderma cellulase. Control sea lettuce (E) and sea lettuce treated with steam explosion (F) (20 mg in 50 mM acetate, pH 5.5) were incubated with purified cellulase (20 µg) in the presence of ß-glucosidase (20 µg) at 37°C for 15 h. As controls, 50 µg of Trichoderma cellulases, meicelase, and onozuka R-10 were used. The data shown are from one of three independent experiments with similar results.