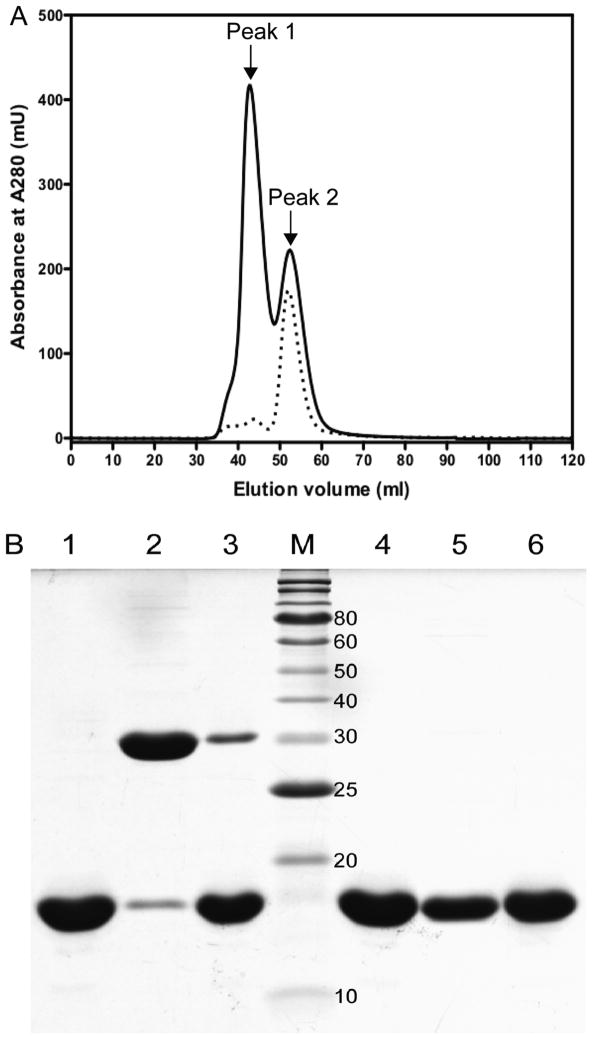
Figure 1.
Separation of dimeric forms rich in cSelS from higher order oligomers rich in cSelS 188Δ by size exclusion chromatography. (A) Elution profiles of cSelS (solid line) and cSelS U188C (dotted line) from a sephacryl S-100 under non-reducing condition. Peak 2, eluted last, contains the selenium-containing form of the enzyme, cSelS. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of cSelS / cSelS 188Δ mixtures following separation by size exclusion chromatography. Lanes 1–3 were run under non-reducing conditions. Lane 1: cSelS U188C (control). Lane 2: cSelS first peak. Lane 3: cSelS second peak. M: Protein molecular weights standard (the molecular mass in kDa is noted on the right). Lanes 4–6 were run under reducing conditions. Lane 4: cSelS U188C (control). Lane 5: cSelS first peak. Lane 6: cSelS second peak.