Figure 2.
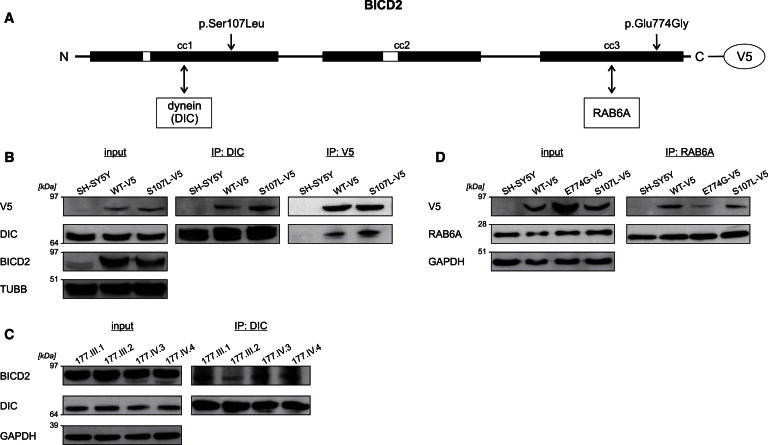
Coimmunoprecipitation of BICD2 and Its Interactors Dynein and RAB6A
(A) Schematic representation of the structure of BICD2. The Ser107 residue is positioned in the N-terminal region that interacts with dynein, whereas the Glu774 amino acid lies within the C-terminal domain that interacts with RAB6A.
(B) Lysates of SH-SY5Y cells stably expressing BICD2-V5 wild-type and altered proteins were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies against dynein intermediate chain 1 (DIC) and V5. The p.Ser107Leu altered BICD2-V5 coprecipitated more with DIC than did the wild-type protein in reciprocal experiments. TUBB was used for showing equal loading of the lysates.
(C) Lysates of lymphoblasts from members of family 177 were immunoprecipitated with DIC antibody and show an increased BICD2 load in the samples of the three affected individuals compared to the healthy relative (177.III.2). GAPDH was used for showing equal loading of the lysates.
(D) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of stable SH-SY5Y cell extracts with RAB6A antibody demonstrates that there is less interaction between RAB6A and p.Glu774Gly altered BICD2-V5 than between RAB6A and the wild-type. The amount of coprecipitated p.Ser107Leu BICD2-V5 was comparable to that of the wild-type. GAPDH was used for showing equal loading of the lysates.
