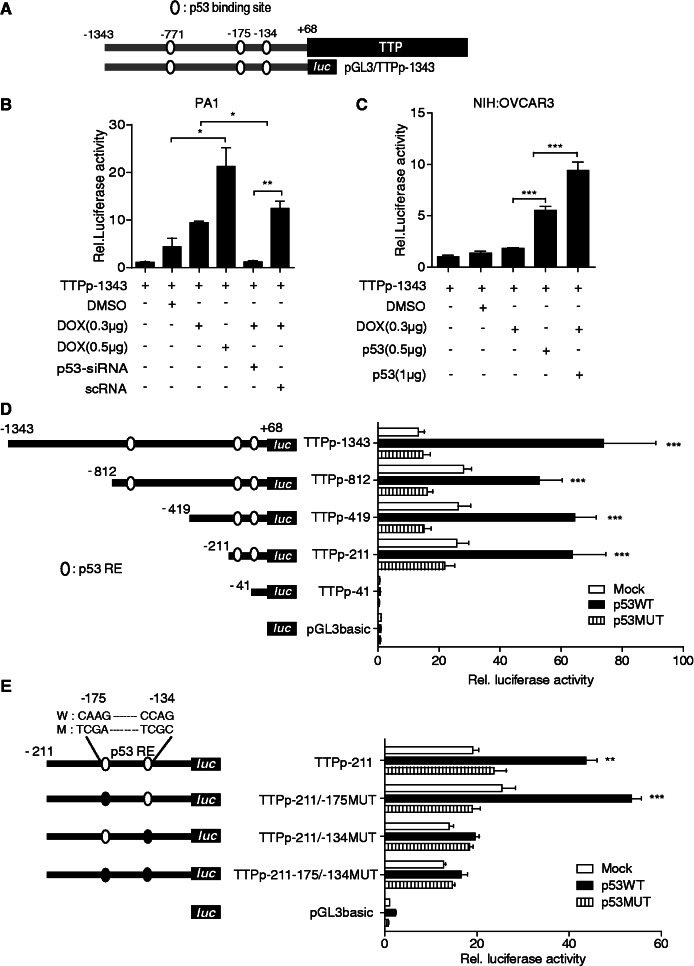
Figure 2.
DOX induces TTP promoter activity in a p53-dependent manner. (A) Schematic structure of the reporter construct pGL3/TTPp-1343. The TTP promoter contains three potential p53 half-sites at positions −771, −175 and −134 relative to the transcription start site. (B, C) DOX induces TTP promoter activity in a p53-dependent manner. (B) PA1 cells were co-transfected with pGL3/TTPp-1343 containing the TTP promoter (−1343 to +68) and p53-siRNA or scRNA. (C) NIH:OVCAR3 cells were co-transfected with pGL3/TTPp-1343 and pCMV-p53WT (p53 wild type) or pCMV-p53MUT (p53 mutant). After treatment with DOX for 24 h, luciferase activity was measured. The expression levels obtained from pGL3/TTPp-1343-transfected cells without DOX treatment were set to 1. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (D, E) p53 half-site at −134 relative to the transcription start site is required for the transcriptional activation of the TTP promoter. (D) Deletion and (E) mutation analysis of the TTP promoter in NIH:OVCAR3 cells. Schematic structures of the deletion and point mutation reporter constructs are shown on the left. Three potential p53 half-sites are indicated with open circles. The point mutations introduced into the binding sites are represented as closed circles. NIH:OVACAR3 cells were co-transfected with the TTP promoter construct and pCMV-p53WT or pCMV-p53MUT. After treatment with DOX for 24 h, cells were lysed and assayed for luciferase activity. The levels of firefly luciferase activity were normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. The expression levels obtained from pGL3 basic-transfected cells were set to 1. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.