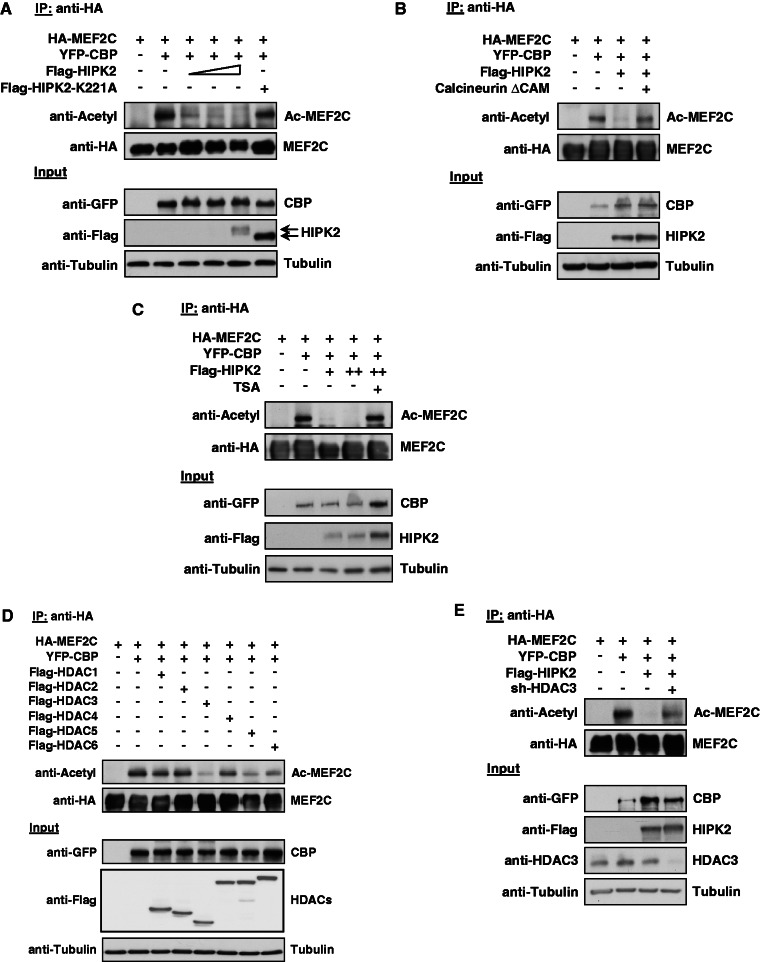
Figure 4.
HIPK2 leads to HDAC3-dependent deacetylation of MEF2C. (A) 293T cells were transfected to express MEF2C along with the acetyl transferase CBP, HIPK2 K221A and increasing amounts of HIPK2. A fraction of the cell lysates was tested for the correct expression of the transfected proteins by western blotting (lower). Equal amounts of protein in the remaining extracts were used for IP with anti-HA antibodies, followed by determination of acetylation using an antibody recognizing acetylated lysines (upper). (B) The experiment was performed similar to the one in (A), but with the exception that cells were transfected with the indicated constructs along with a constitutively active form of the phosphatase Calcineurin (Calcineurin ΔCAM) (C) The experiment was done as in (A), but cells coexpressing MEF2C, CBP and HIPK2 were also incubated for 6 h in the presence of 1 μM TSA as shown. (D) The indicated combinations of MEF2C, CBP and the different HDAC proteins were coexpressed in 293T cells, followed by IP of MEF2C with anti-HA antibodies and the analysis of MEF2C acetylation by immunoblotting (upper). The lower part shows correct expression of the transfected proteins. (E) 293T cells were transfected with vectors for a HDAC3-specific shRNA or the empty vector as a control, followed by selection of transfected cells with puromycin for 3 days. Cells were replated and then transfected to express the indicated combinations of MEF2C, CBP and HIPK2 together with the shRNA-producing plasmids as shown. Cell lysates were analyzed for acetylation of immunoprecipitated MEF2C (upper) and for correct protein expression (lower) as shown.