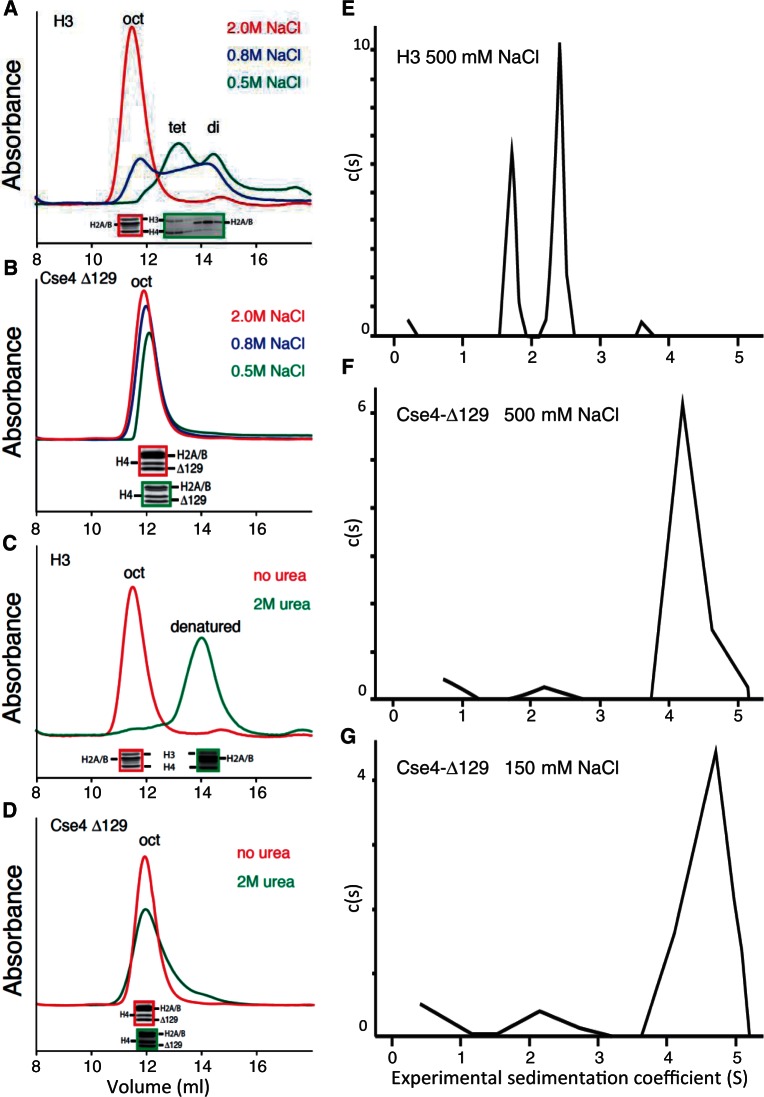
Figure 1.
Cse4 octamers resist dissociation in low-salt and denaturing conditions. (A and B) Superdex 200 gel-filtration chromatography of octamers containing (A) H3 or (B) (tail-deleted) Cse4-Δ129 following equilibration of the column with 2.0 (red), 0.8 (blue) or 0.5 M (green) NaCl. (C and D) Same as (A and B) except that the column was equilibrated with either 2 M NaCl (red) or 2 M NaCl + 2 M urea (green). Red- and green-bordered insets show SDS–PAGE Coomassie-stained images of corresponding peak fractions. In each panel, exactly the same sample was injected into the column; however, non-specific absorption to the column increases with lower salt concentrations, resulting in slightly lower recovery of total proteins. (E–G) Sedimentation velocity analyses of octamers containing H3 in 500 mM NaCl (E), Cse4-Δ129 in 500 mM NaCl (F) or Cse4-Δ129 in 150 mM NaCl (G).