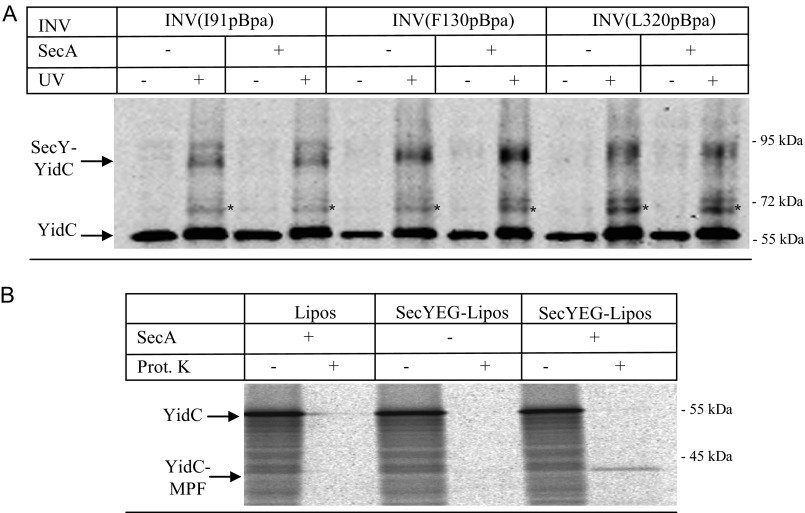
FIGURE 6.
The SecY-YidC interaction is not influenced by SecA-binding to SecY. A, INVs from BL21 or C43 cells expressing SecY derivatives with pBpa incorporated at the indicated positions were isolated by sucrose gradient centrifugation and adjusted to a final SecY concentration of approximately 6 μm. These INV were incubated with either 6 μm purified SecA or with buffer (−) and UV exposed or kept in the dark. Subsequently, SecY and its cross-linking products were purified via metal affinity chromatography. INVs were separated on SDS-PAGE and after Western transfer decorated with α-YidC antibodies. Asterisk (*) indicates the second UV-dependent SecY-YidC cross-linking product at 72 kDa. B, the functionality of SecA was tested with reconstituted proteoliposomes. YidC was in vitro synthesized in the presence of either liposomes (Lipos) or liposomes reconstituted with SecYEG. When indicated, SecA was present during in vitro synthesis and transport. After 30 min of synthesis at 37 °C, the samples were split in half and one part was directly precipitated with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) (−). The other half was first treated for 20 min at 25 °C with 0.5 mg/ml of proteinase K (Prot. K) and only then TCA precipitated. YidC and its membrane-protected fragment (YidC-MPF) are indicated. The YidC-MPF corresponds to the first two transmembrane domains of YidC plus the connecting 325-amino acid long periplasmic loop (37).