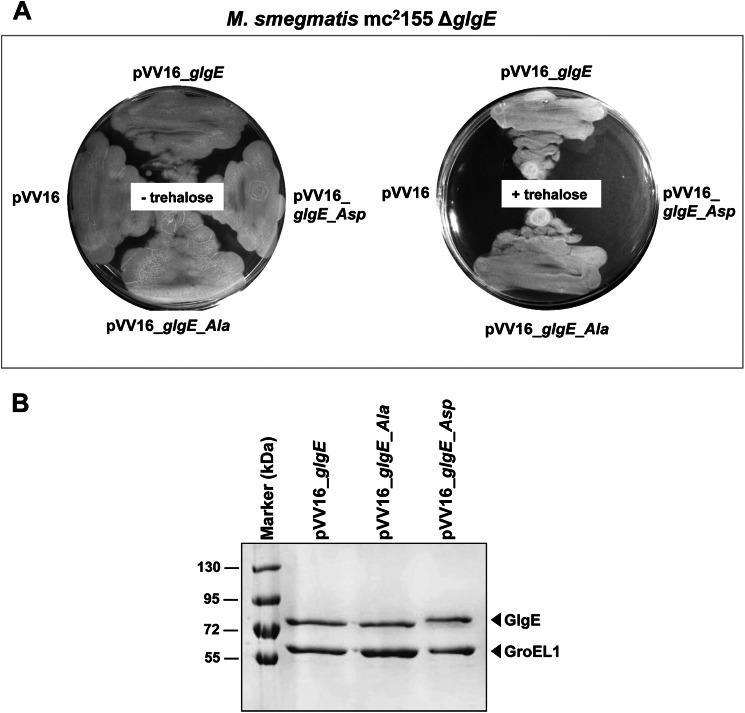
FIGURE 4.
A, functional complementation of M. smegmatis ΔglgE with GlgE or GlgE_Ala but not with phosphomimetic GlgE_Asp. The ΔglgE mutant of M. smegmatis, which is sensitive to trehalose, was transformed with pVV16, pVV16_glgE, pVV16_glgE_Ala, or pVV16_glgE_Asp and grown with or without trehalose (1 mm). Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 4–5 days. B, expression of the different GlgE variants in the complemented M. smegmatis ΔglgE strains. GlgE proteins from M. smegmatis ΔglgE cultures complemented with the wild-type pVV16_glgE, pVV16_glgE_Ala, or pVV16_glgE_Asp constructs were obtained by purification by nickel affinity chromatography. Equal quantities of purified His-tagged GlgE proteins per unit volume of culture were separated by SDS-PAGE, stained with Coomassie Blue, and identified using mass spectrometry. The mycobacterial GroEL1 protein was co-purified due to it harboring a region rich in histidine residues, thus providing an internal standard. Marker indicates molecular mass markers.