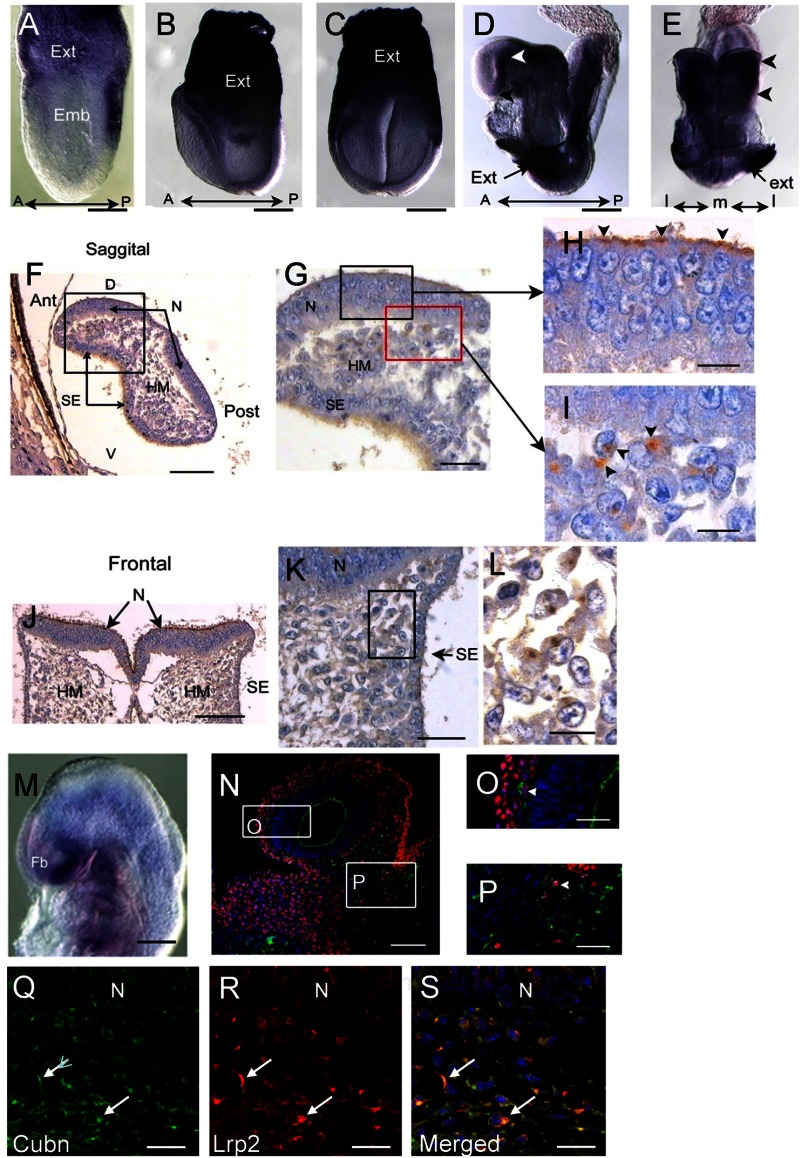
FIGURE 1.
Cubn distribution in the early mouse embryo. A–C, strong Cubn mRNA expression in the extra-embryonic (Ext) tissues during gastrulation (A, lateral view) and early headfold stages (B and C, lateral and frontal views). D–L, Cubn mRNA and protein expression at E8.5; Cubn is found in the forebrain (white arrowhead in D, lateral view) and the cephalic mesenchyme (arrowheads in E, frontal view); black arrowhead in D points to the ANR. F–L, sagittal (F–I) and frontal (J–L) paraffin sections through the forebrain show Cubn distribution at the apical pole of neuroepithelial cells (arrowheads in H) and at the plasma membrane of mesenchymal cells (arrowheads in I). M, Cubn mRNA (lateral view) in the forebrain (Fb), the cephalic mesenchyme of the fore-, mid-, and hindbrain regions, and the pharyngeal region at E9.0. N–P, sagittal cryosection of an E9.0 embryo shows partial co-localization of Cubn (green) and Tfap2α (red) in the migratory neural crest at the level of the forebrain (O) and midbrain (P) mesenchyme. Cubn is also detected in the forebrain (N and O). Q–S, Cubn (in green) and Lrp2 (in red) co-localize in the migratory neural crest of the same embryo (arrows). A, anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral; m, medial; l, lateral; emb, embryonic; hm, head mesenchyme; N, neuroepithelium; se, surface ectoderm. Scale bars, A, 175 μm; B and C, 200 μm; D and E, 250 μm; F and J, 125 μm; G and K, 80 μm; H, I, and L, 50 μm; M, 250 μm; N, 175 μm; O and P, 75 μm; Q–S, 15 μm.