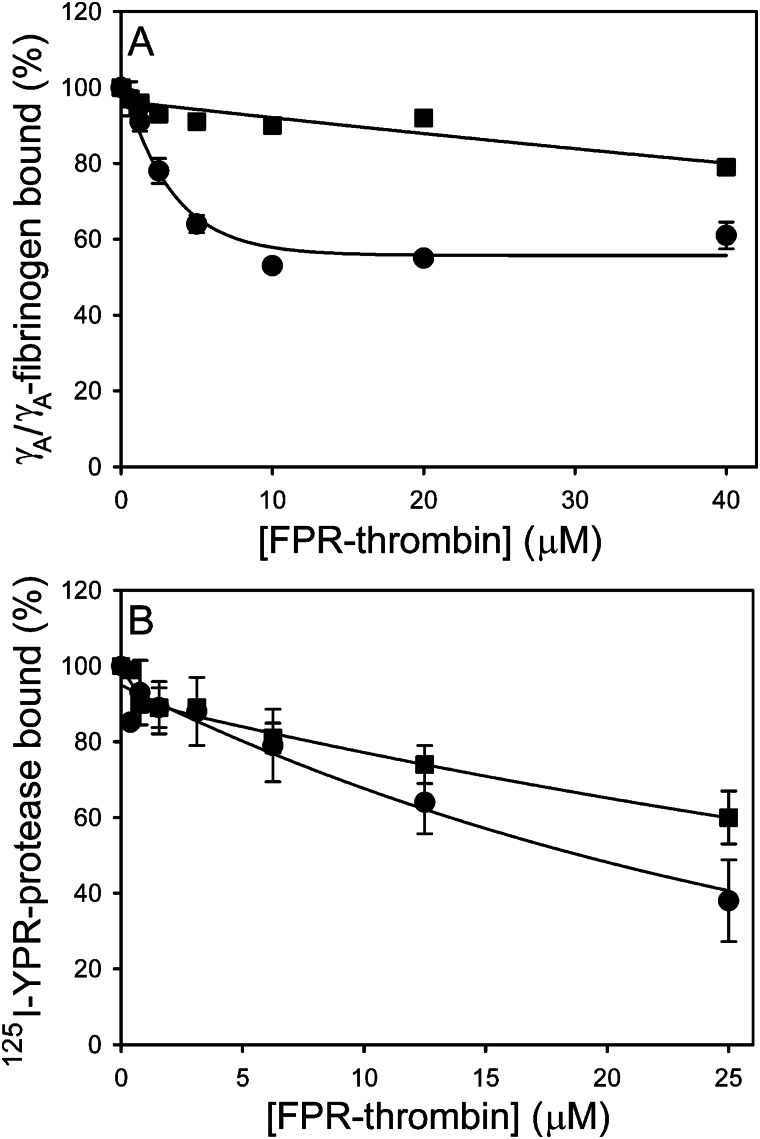
FIGURE 6.
Effect of FPR-thrombin on batroxobin binding to γA/γA-fibrinogen or γA/γA-fibrin clots. A, effect of FPR-thrombin on γA/γA-fibrinogen binding to immobilized FPR-batroxobin was determined using SPR. γA/γA-fibrinogen (2.5 μm) was incubated with FPR-thrombin concentrations up to 40 μm in the absence (●) or presence (■) of 80 μm hirudin, and the mixture was then injected into flow cells containing immobilized FPR-batroxobin. Binding in the presence of competitors was normalized relative to that determined in their absence. Data are plotted as the percentage of γA/γA-fibrinogen bound versus the FPR-thrombin concentration. B, binding of 125I-YPR-batroxobin (■) and 125I-YPR-thrombin (●) to γA/γA-fibrin clots was measured in the absence or presence of FPR-thrombin concentrations up to 25 μm. Clots were formed by incubating 2 or 0.06 μm γA/γA- fibrinogen with 20 nm 125I-YPR-thrombin or 40 nm 125I-YPR-batroxobin, respectively, and 10 nm thrombin. After 60 min, clots were counted for radioactivity to quantify bound 125I-YPR-protease. Data are plotted as the percentage of 125I-YPR-protease bound versus the FPR-thrombin concentration. Data points represent the mean ± S.D. of 3–4 experiments, and the lines represent nonlinear regression analyses.