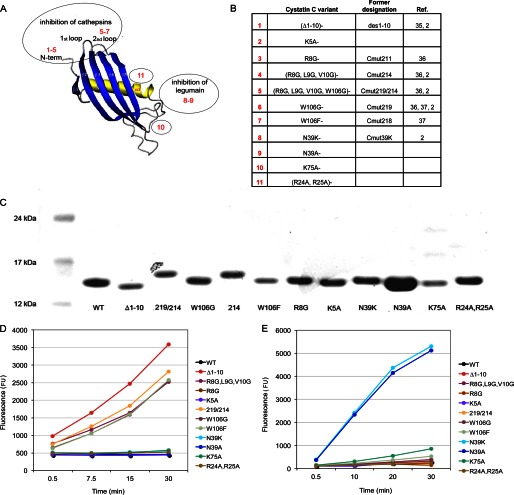
FIGURE 1.
Characteristics of cystatin C variants. A, schematic cystatin molecule (adopted from Ref. 34). Cystatin C variants 1–7 have amino acid substitutions in parts of the molecule involved in cysteine cathepsin inhibition. In variants 8 and 9, the amino acid residue in position 39 is substituted, which influences legumain inhibition. Variants 10 and 11 have substitutions of amino acids not considered to participate in enzyme inhibition. B, description of the amino acid substitutions of the cystatin C variants used in the study. C, analysis of cystatin C variants by SDS-PAGE after reduction in a 4–12% Bis-Tris polyacrylamide gel. Lane 1: size marker. Lane 2: wild-type cystatin C. Lanes 3–13: cystatin C variants after final purification. D, inhibition of cathepsin B activity by cystatin C variants monitored by the fluorescent substrate Z-Phe-Arg-NMec. Variants 1, 4, 5, 6, and 7 (curves for 6 and 7 are overlapping) did not inhibit cathepsin B, as they contained serial amino acid substitutions in the cysteine cathepsin binding site. E, inhibition of legumain by cystatin C variants assayed using the fluorescent substrate Z-Ala-Ala-Asn-NMec. Variants 8 and 9 did not inhibit legumain, as the side-chain of residue N39 is important for legumain inhibition.