Fig. 4.
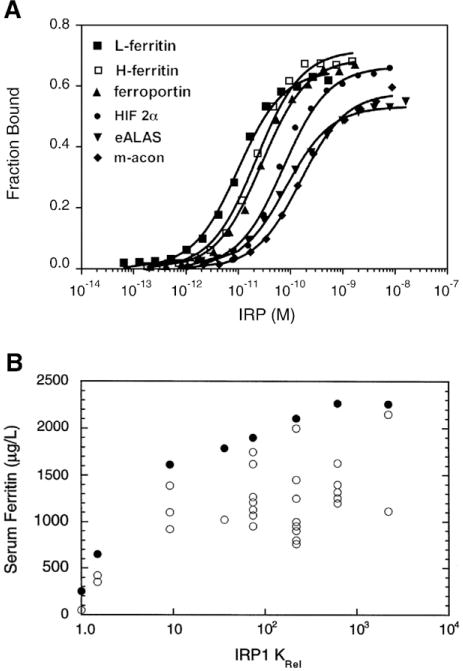
Altered affinity of IRP1 for mutant and natural IREs. A) The affinity of interaction of IRP1 for six vertebrate 5′ IREs as determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) [108]. The KD for these IREs varied over a 9-fold range. B) Mutations in the human L-ferritin IRE were identified in seven patients with hereditary hyperferritinemia–cataract syndrome. The affinity of interaction of IRP1 with mutant human L-ferritin IREs was determined by EMSA and related to serum ferritin values reported for each patient on different occasions (open circles) [113]. Maximal serum ferritin for each patient (closed circles). Results on the x-axis are expressed as Krel which is KD,mutant/KD,wildtype and higher values for Krel indicate lower binding affinity of the mutant IRE with IRP1. Note the steeper slope of the relationship between serum ferritin and Krel over the range 1 to 10 for Krel.
A similar observation was made for IRP2 [113].
