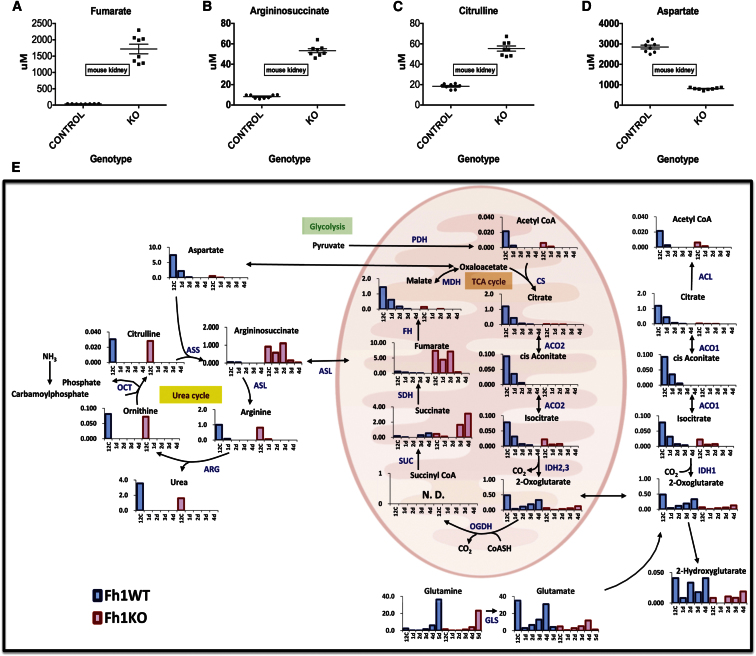
Figure 1.
FH-Deficient Cells Synthesize Argininosuccinate Directly from Fumarate
(A–D) Concentrations of specific urea cycle metabolites (μM) in control and FH1KO kidneys as determined by CE-TOFMS (Soga et al., 2009). All differences between control and FH1KO mice were significant (p < 0.01, Student’s t test). For metabolomic analyses, six mice aged 15 weeks were analyzed from each group.
(E) CE-TOFMS analyses of deuterium label incorporation into key Krebs cycle and urea cycle metabolites in FH1WT (blue) and KO (red) MEFs after 9 hr incubation in culture containing [D5]-glutamine. Transit of label through the canonical oxidative Krebs cycle would result in 2OG+4, succinate+4, fumarate+2, malate+2, and Asp+1, while reductive carboxylation of glutamate would result in isocitrate m+2, citrate m+2, and aspartate m+1. We did not observe label enrichment in citrate, so the reductive mechanism is not used for citrate synthesis. Argininosuccinate produced from arginine and fumarate has m+2, whereas that produced from citrulline and aspartate has m+1. We detected predominantly argininosuccinate m+2, which has a similar isotopomer distribution pattern to fumarate, suggesting it is synthesized directly from fumarate.
For each graph, the concentration of metabolites (fmol/cell) is indicated on the y axis and label enrichment of [D5]-glutamine in FhWT and KO MEFs are represented on the x axis in the following order: 12C, 12C-1d, 12C-2d, 12C-3d, and 12C-4d. See also Table S1 for absolute metabolite levels.
ACL, ATP citrate lyase; ACO1, -2, aconitase 1, -2; IDH1, -2, -3, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1, 2, 3; CS, citrate synthase; SUC, succinyl CoA synthetase; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; OGDH, oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; FH, fumarate hydratase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; GLS, glutaminase; ASS, argininosuccinate synthase; ASL, argininosuccinate lyase; OCT, ornithine carbamoyltransferase; ARG, arginase.