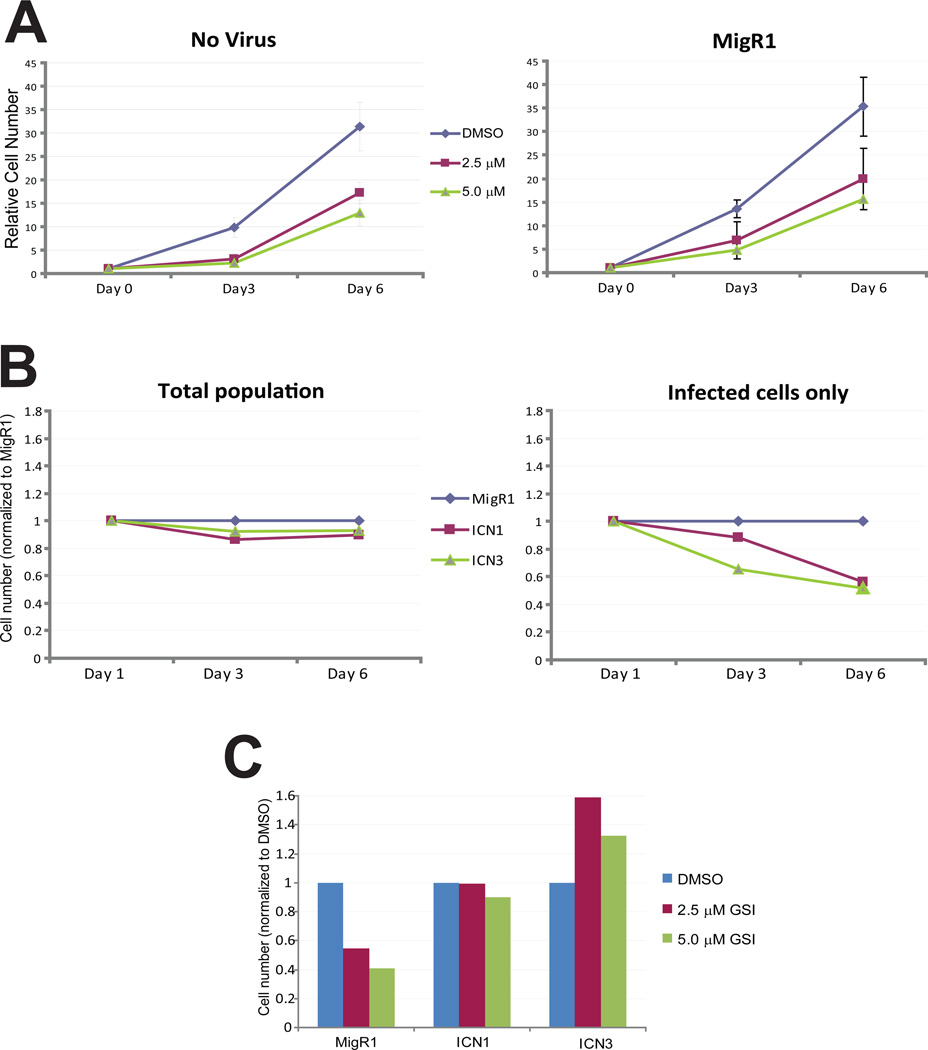
Figure 4. Notch signaling rescues cells from the growth inhibitory effects of GSI.
(A) Retroviral infection has no effect on growth inhibition of NB507 PDAC cells by MRK-003. Cell number was determined 3 days or 6 days following treatment with the GSI (left panel); infection with MigR1 retrovirus did not alter the dose-response curve. (B) Cell number was determined following infection with control (empty) MigR1 virus, or virus encoding a constitutively active form of Notch1 (ICN1) or Notch3 (ICN3). ICN1 and ICN3 expression had minimal effects on NB507 cell number compared to MigR1 when the total population was examined (left panel); when only infected cells were measured, ICN1and ICN3 had a mild inhibitory effect on growth (right panel). (C) ICN1 and ICN3 prevented GSI-induced growth inhibition after 6 days of treatment (only infected cells are shown). These results are representative of two independent experiments.