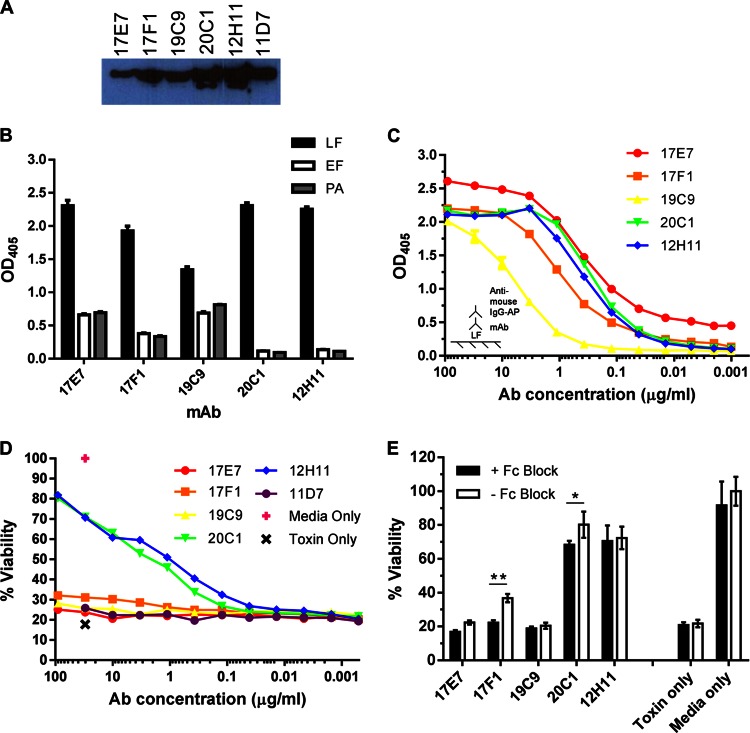
Fig 2.
In vitro characterization of MAbs to LF. Six LF-specific MAbs were purified from cell lines generated from a standard splenocyte-myeloma fusion. (A) Immunodetection of LF. MAbs, diluted 1:500, were incubated with purified LF on a nitrocellulose membrane and detected by chemiluminescence with HRP-conjugated secondary Abs. (B) IgG MAb reactivity to anthrax toxin components. Binding to LF, EF, and PA was measured by ELISAs in triplicate for each Ab; plates were coated with 2 μg/ml antigen and incubated with 10 μg/ml antibody. Ab binding was detected with AP-conjugated secondary Abs. (C) Relative binding capacity of IgG MAbs to LF as determined by ELISA. The ELISA plate was coated with 2 μg/ml LF, and MAb concentrations were titrated 1:3 from 90 μg/ml. (D) In vitro cytotoxicity assay to measure MAb-mediated toxin protection. J774 macrophages were incubated with 0.1 μg/ml LeTx with or without MAbs at various concentrations. Cells were incubated with toxin alone or toxin-free medium as negative and positive controls, respectively, for viability. (E) Cell viability assay with Fc receptors blocked. The assay was performed as described above, with 0.1 μg/ml LeTx, except cells were incubated with 100 μl of 10 μg/ml Fc Block for 15 min prior to incubation with LeTx and MAbs. *, cell viability was significantly lower with Fc Block for 20C1 (P = 0.0077); **, P < 0.0001 for 17F1.