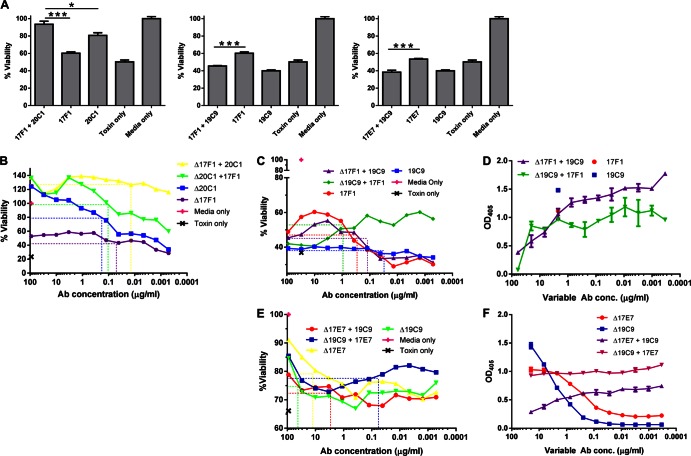
Fig 4.
Combinatory effects of LF MAbs on lethal toxin neutralization. (A) Macrophage viability assay of anti-LF MAbs in pairs. J774 cells were incubated with 0.1 μg/ml LeTx and 10 μg of each Ab. ***, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. (B) Cell survival assay titrating 17F1 in combination with 20C1. Cells were incubated with 0.1 μg/ml LeTx and 30 μg/ml of the constant MAb mixed with titrated amounts of the variable MAb. (C) Cell survival assay of 19C9 and 17F1 in combination. Cells were incubated with 0.1 μg/ml LeTx and 30 μg/ml of the constant MAb and titrated 1:3 with the variable Ab starting with 90 μg/ml. (D) Competition ELISA between 17F1 and 19C9. A 96-well plate was coated with 2 μg/ml LF and then incubated with 2 μg/ml of one MAb (constant concentration) and a variable concentration of the other. Binding of the constant MAb was detected with an isotype-specific AP-conjugated secondary Ab. (E) MTT assay with 17E7 and 19C9. The assay was performed as described for panels B and C. (F) Competition ELISA between 17E7 and 19C9. Dashed lines indicate the MAb concentration at 50% of maximum cell survival for each of the survival curves shown in panels B, C, and E.