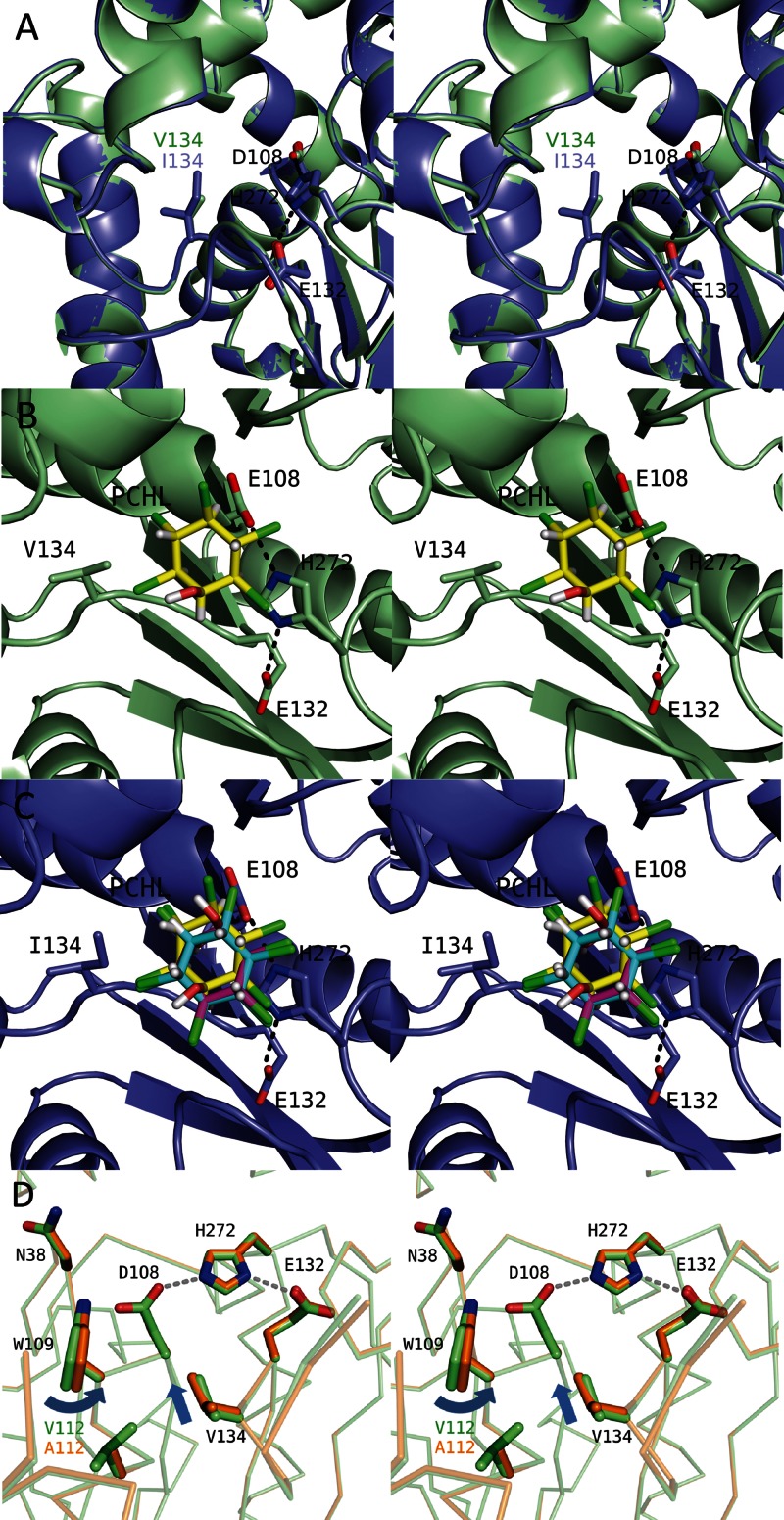
Fig 4.
Different amino acid residues located around the active site between LinBMI and LinBUT. (A) Superimposition of the active sites of the wild type (light green) and the V134I mutant (slate) of LinBMI. The catalytic triad residues (D108, E132, and H272) and V134/I134 are labeled. (B and C) Docking simulations of the wild type (B) or the V134I mutant (C) with PCHL. The chlorine, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms of the PCHL molecules are colored green, red, and white, respectively. In wild-type LinBMI, the PCHL model with the lowest binding energy is shown, and its carbon atoms are colored yellow. In the V134I mutant, the carbon atoms are colored cyan, magenta, and yellow in the PCHL models with the lowest binding, the second-lowest binding and the highest interation energies, respectively. (D) Superimposition of the active sites between the wild type (light green) and the V112A mutant (orange).