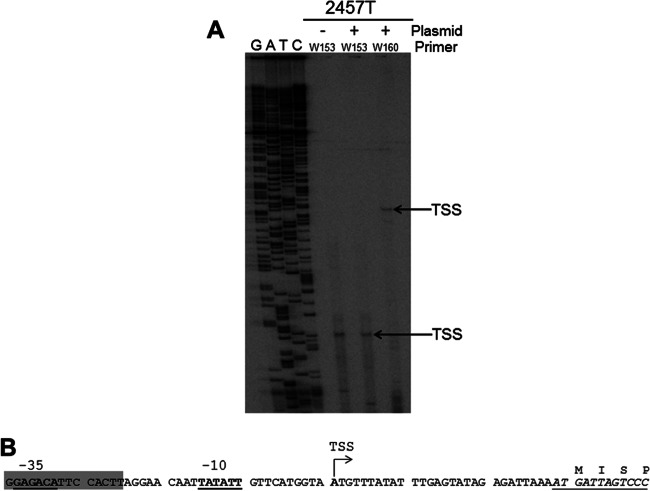
Fig 2.
Identification of the transcription start site of the ospZ gene. (A) Primer extension analysis of ospZ transcripts generated by the wild type (2457T) or the wild type carrying the plasmid pDB05. The primer W153 binds within ospZ, and the primer W160 binds within lacZ. Arrows indicate identified transcription start sites, which map to the same nucleotide position. (B) Sequence of the ospZ promoter region and beginning of the gene. The ospZ transcription start site identified by this work is indicated (bold type and designated TSS), and associated potential −10 and −35 elements are shown (bold and underlined). The gene sequence is italicized, and encoded amino acids are given. The sequence bearing strong sequence similarity to the 3′ end of IS3 (92% identity over 185 nt) is highlighted in gray (GenBank number AL391753.1 [32]).