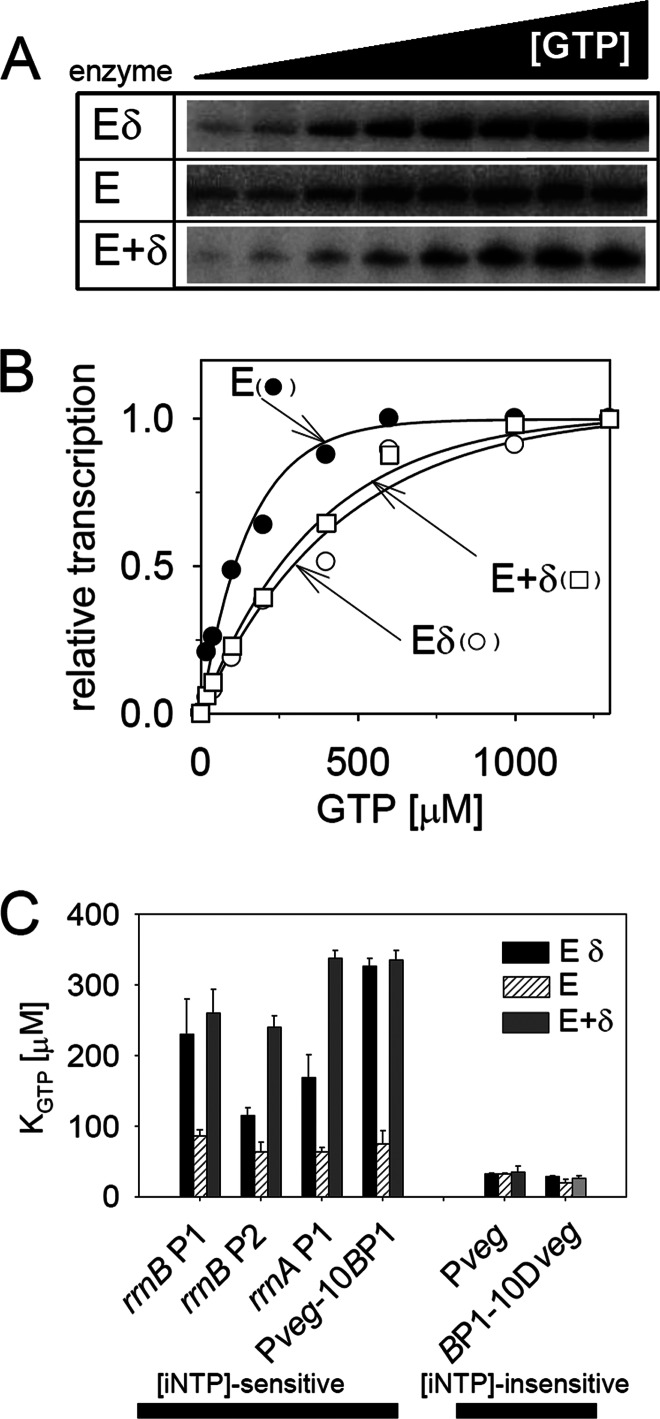
Fig 1.
δ changes the requirements of RNAP for the [iNTP] at some promoters in vitro. (A) Gels showing primary data from in vitro multiple-round transcriptions from rrnBp1 (LK7) with three types of RNAP: Eδ, E, and E+δ. Eδ is RNAP purified from wt B. subtilis containing δ; E is RNAP purified from a ΔrpoE strain without δ; E+δ is E with added purified δ in a 1:5 molar ratio. The concentration of the iNTP (GTP) varied from 20 to 2,000 μM. (B) Quantitation of the data from panel A. Open circles, Eδ; filled circles, E; open rectangles, E+δ. The plateau of the maximal transcription activity with each enzyme was set as 1. (C) Comparison of KGTP values of rrnBp1 (LK7), rrnBp2 (LK140), rrnA P1 (LK14), Pveg-10BP1 (LK4), Pveg (LK1), and BP1-10Dveg (LK9). Eδ (black bars), E (bars with diagonal lines), and E+δ (dark gray bars) are the three forms of RNAP used in the assays illustrated in panels A through C. The KGTP constant specifies the concentration of GTP required for 50% maximal transcription. The bars represent mean values of at least two independent experiments.