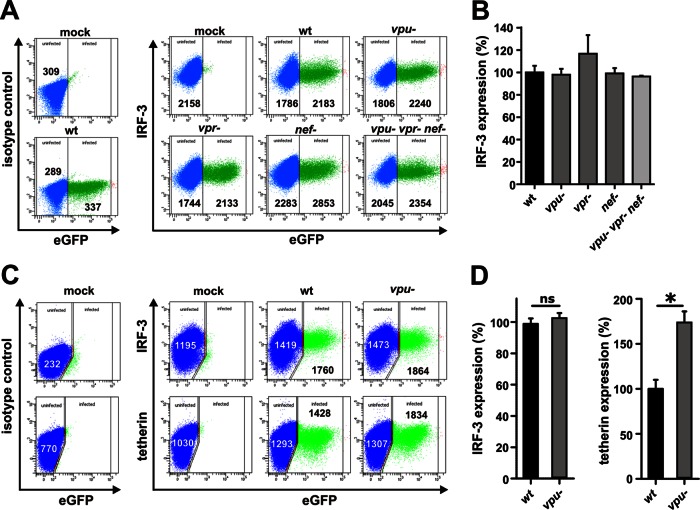
Fig 3.
Lack of vpu, nef, or vpr expression does not affect IRF-3 expression levels in HIV-1-infected T cells. (A) SupT1 cells were infected with virus stocks of different NL4-3 IRES eGFP mutants. At 3 days postinfection, cells were permeabilized and stained for IRF-3 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) to perform FACS analysis. (B) Levels of IRF-3 expression in cells infected with the indicated mutant NL4-3 constructs relative to the wild-type virus (wt; set as 100%). Data are means (± standard errors of the means [SEM]) derived from three independent experiments. (C) PBMCs were transduced with VSV-G-pseudotyped virus stocks of wild-type or vpu-defective NL4-3 IRES eGFP mutants. PBMCs were stimulated with interleukin-2 and phytohemagglutinin for 3 days prior to transduction. At 3 days postransduction, the cells were permeabilized and stained for IRF-3 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or tetherin (eBioscience) for FACS analyses. (D) Mean levels (± SEM; n = 3) of IRF-3 and tetherin expression in cells transduced with the vpu-defective virus relative to the wild-type control (set as 100%) are indicated.