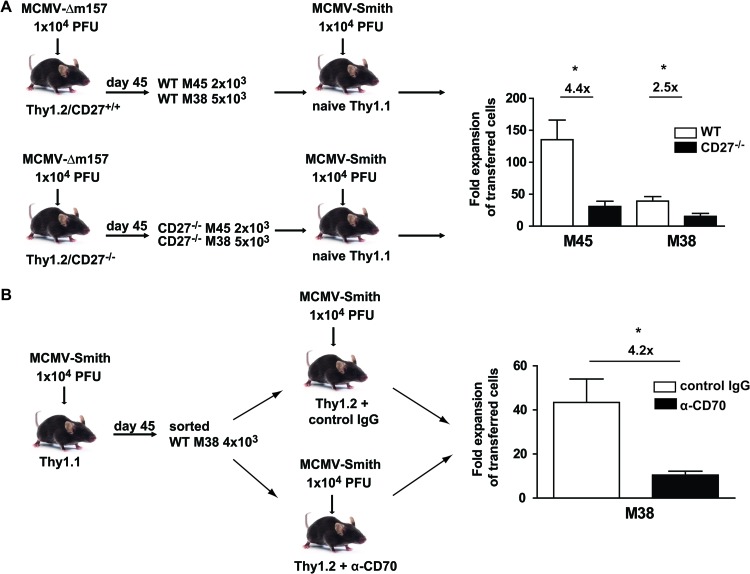
Fig 9.
CD27-CD70 costimulation is important for secondary expansion of MCMV-specific CD8+ T cells. (A) WT and CD27−/− mice were infected with 1 × 104 PFU MCMV-Δm157. At day 45 postinfection, M45 and M38 tetramer+ cells were isolated from the spleen and transferred into naive Thy1.1 hosts, which were subsequently infected with 1 × 104 PFU MCMV-Smith. On day 7 after infection, the expansion of donor M45- and M38-specific CD8+ T cells in the spleen was determined by MHC class I tetramer staining. The fold expansion of WT and CD27−/− M45- and M38-specific CD8+ T cells was determined by dividing the absolute numbers of Thy1.2+ tetramer+ CD8+ T cells by the number of cells that were used for the adoptive transfer. Fold differences are indicated. (B) Thy1.1 donor mice were infected with 1 × 104 PFU MCMV-Smith, and at day 45 postinfection, splenic M38 tetramer+ cells were transferred into naive Thy1.2 hosts, which were subsequently infected with 1 × 104 PFU MCMV-Smith. Before and during infection, mice received a blocking anti-CD70 or control antibody. At day 7 postinfection, the fold expansion of M38-specific CD8+ Thy1.1+ T cells was determined. Fold differences are indicated. All bar graphs show means and SEM. Statistical significance was determined by the Student t test (*, P < 0.05; n = 4).