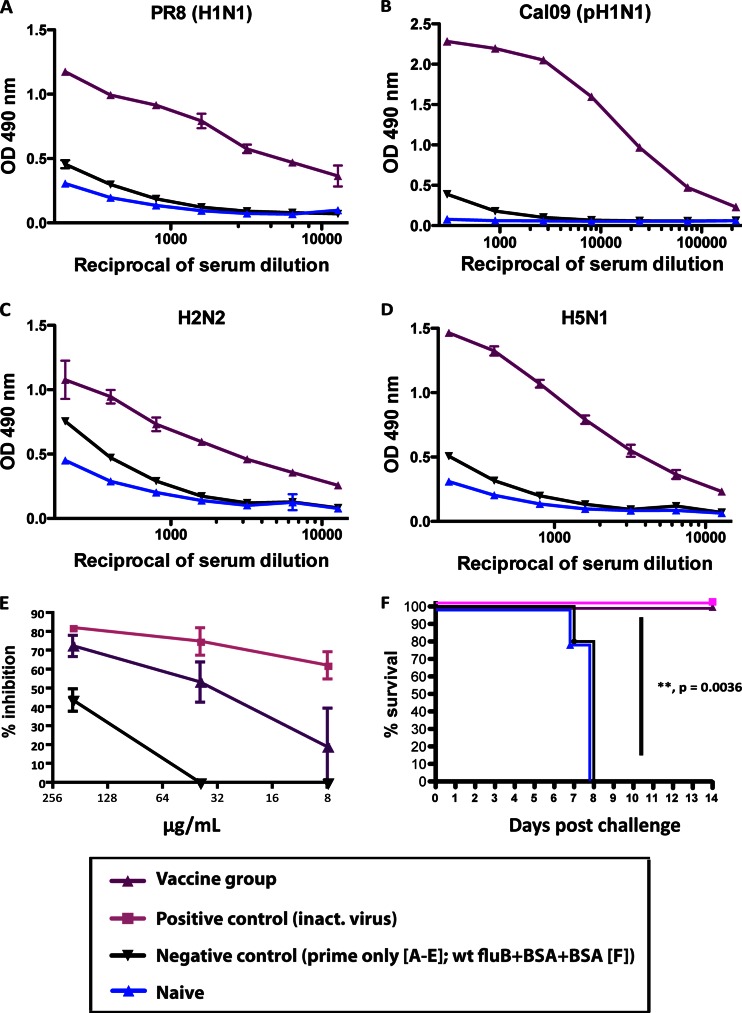
Fig 4.
The antibodies elicited by sequential vaccination with chimeric HAs are cross-reactive against group 1 HAs and have neutralizing activity in vitro and in vivo. (A to D) Stalk-specific ELISA reactivities of sera from animals electroporated with cH9/1 DNA and then vaccinated with cH6/1 and cH5/1 (replaced by H1 for mice used for panel C) soluble proteins (purple triangles) or BSA (black triangles) or of sera from naive animals (blue triangles) against H1 HA (purified PR8 [H1N1] virus substrate) (A), pH1 HA [purified Cal09 (pH1N1) protein substrate] (B), H2 HA (purified H2N2 virus substrate) (C), and H5 HA (purified H5N1 virus substrate) (D). (E) Animals were vaccinated as described above. Total IgG was purified for use in an H2-based pseudoparticle entry inhibition assay. Percent inhibition was assessed as the decrease in luciferase expression compared to that of controls. The Fab fragment of CR6261 (pink squares) was used as a positive control. (F) Passive transfer assay. Naive mice received sera from PR8-vaccinated animals (green squares; n = 5), fluB-cH9/1+cH6/1+cH5/1-vaccinated animals (purple triangles; n = 5), wt fluB+BSA+BSA-vaccinated animals (black triangles; n = 5), or naive mice (blue triangles; n = 5) via intraperitoneal injection and were then challenged with PR8 (H1N1) virus. The Kaplan-Meier curve depicts survival (P = 0.0036 between the groups that received sera from fluB-cH9/1+cH6/1+cH5/1-vaccinated animals and the wt fluB+BSA+BSA group).