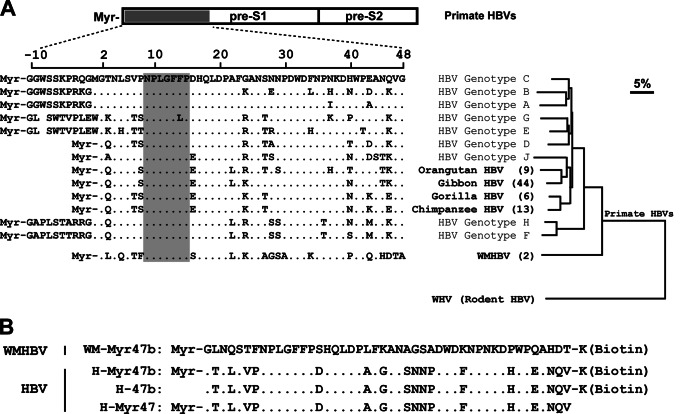
Fig 1.
Sequence alignment of the pre-S1 N-terminal domain of primate hepadnaviruses and phylogenetic analysis of the L proteins. (A) Amino acid sequences of the receptor-binding region (aa −10 to 48 or 2 to 48) in the pre-S1 domain of human HBVs were aligned with the corresponding regions of other primate HBVs. The residue numbering was based on HBV genotype D. The GenBank accession numbers of the hepadnaviruses compared herein are as follows: HBV genotype A, JQ687533; genotype B, JX978431; genotype C, AY167095; genotype D, X02496; genotype E, GQ161835; genotype F, DQ899142; genotype G, AP007264; genotype H, AB205010; genotype J, AB486012; chimpanzee HBV, AF222322; gorilla HBV, AJ131567; orangutan HBV, EU155825; gibbon HBV, U46935; WMHBV, AY226578. For nonhuman primate HBVs, the values in parentheses are the numbers of recorded complete genomes of the corresponding viruses. The receptor-binding motif of human HBV (aa 9 to 15) and the corresponding regions of other primate HBVs are shaded in gray. The phylogenetic tree was based on the amino acid sequences of the L proteins of the compared primate HBVs and woodchuck hepatitis virus (GenBank accession number J02442), a rodent hepadnavirus. The distance along the horizontal axis among isolates is proportional to the amino acid divergence. The scale bar (upper right) represents 5% divergence. (B) Amino acid sequences of four synthetic peptides used in this study. The peptide WM-Myr47b corresponds to aa 2 to 47 of the L protein of WMHBV (GenBank accession number AY226578). The amino acid sequences of the three HBV peptides are derived from aa 2 to 47 of the L protein of the genotype C isolate (GenBank accession number AY167095). Peptides of this region were synthesized with or without a lysine residue at the C terminus for biotinylation and with or without myristoylation modification at the N terminus. Myr, myristoyl group.