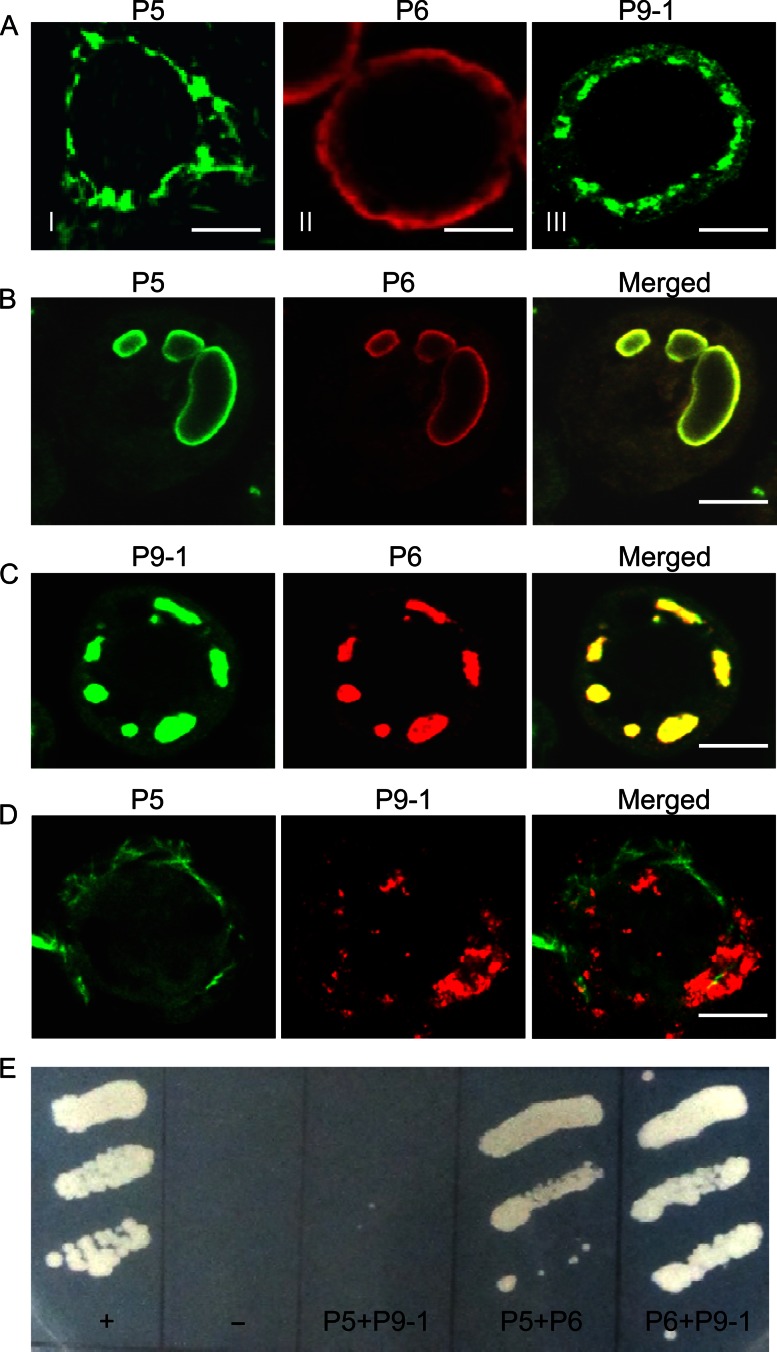
Fig 5.
SRBSDV P6 was associated with inclusions formed by P5 or P9-1 through protein-protein interactions. (A to D) Subcellular localization of nonstructural proteins P5, P6, and P9-1 in the absence of viral infection. Sf9 cells infected with recombinant baculoviruses containing P5, P6, or P9-1 were fixed 3 days after infection and prepared for immunofluorescence microscopy. Cells were immunostained with P5-FITC, P6-rhodamine, P9-1–FITC, or P9-1-*rhodamine. (A) P5 formed filament-like structures (frame I), P6 was distributed diffusely in the cytoplasm (frame II), and P9-1 formed punctate structures (frame III). Bars, 5 μm. (B) P6 and P5 were colocalized on large circular structures when coinfected with recombinant baculoviruses containing either P6 or P5. Bar, 5 μm. (C) P6 and P9-1 colocalized to punctate structures when coinfected with recombinant baculoviruses containing either P6 or P9-1. Bar, 5 μm. (D) The filament-like structures of P5 were not associated with the punctate structures of P9-1 when coinfected with recombinant baculoviruses containing either P5 or P9-1. Bar, 5 μm. (E) Yeast two-hybrid assay of protein-protein interactions among the SRBSDV P5, P6, and P9-1 proteins. Transformants were plated onto synthetic defined minimal medium minus leucine, tryptophan, histidine, and adenine (SD/−Leu/−Trp/−His/−Ade) for 4 days. +, positive control, i.e., pTSU2-APP/pNubG-Fe65; −, negative control, i.e., pTSU2-APP+pRR3-N; P5+P9-1, pBT3-STE-P5+pPR3-N-P9-1; P5+P6, pBT3-STE-P5+pPR3-N-P6; P6+P9-1, pBT3-STE-P6+pPR3-N-P9-1.