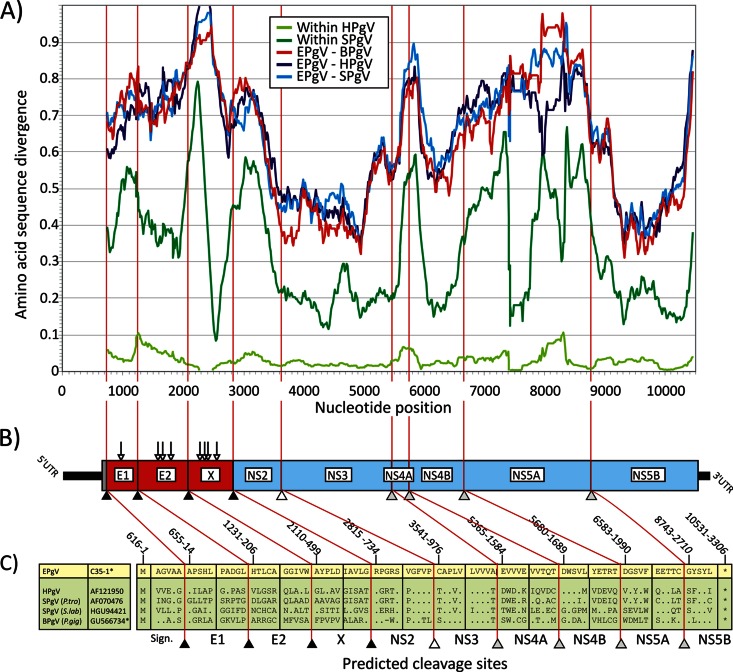
Fig 1.
(A) Amino acid sequence divergence between EPgV and HPgV, SPgV, and BPgV based on 201-nt fragments in 6-nt increments across the genome alignment (midpoint plotted on the y axis). Within-species distances for HPgV and SPgV are included for comparison. The divergence scan commenced at the predicted signalase cleavage site at the start of the E1-encoding genes. (B, C) Genome diagram of EPgV showing predicted N-linked glycosylation sites (Nx[S/T]; vertical arrows) and proposed cleavage sites (sequence positions were numbered on the basis of the EPgV sequence). Cleavage sites in the EPgV polyprotein and in other pegiviruses were predicted by alignment and homology to sites previously identified in SPgV (sites NS3/NS4A, NS4A/NS4B, NS4B/NS5A, and NS5A/NS5B) and by comparison with predicted signalase sites between structural proteins and the NS2/NS3 cleavage site of BPgV. Potential signalase sites in EPgV were evaluated by using the SignalP 4.1 server, which identified homologous cleavage sites that aligned with those in BPgV, including the boundaries of the novel proposed X protein.