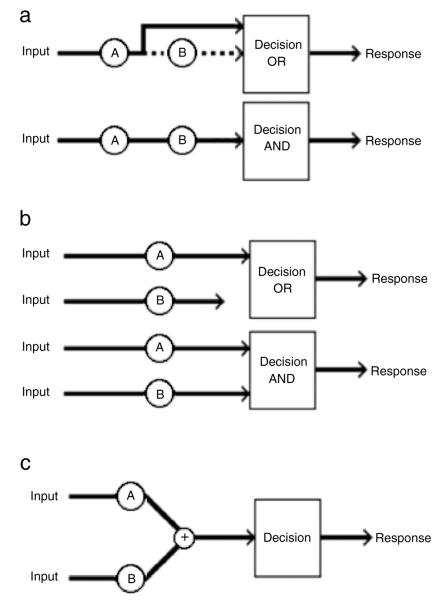
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustrations of the three canonical processing architectures: (a) serial, (b) parallel, and (c) coactive. For the serial and parallel models, both the minimum-time (OR) and exhaustive (AND) stopping rules are illustrated. For the serial OR model, the dashed line indicates that completion of the associated item (channel, etc.) was not needed, because the system responded to the first item processed. In the coactive model, decisions are made when the summed information from the two items exceeds some threshold.