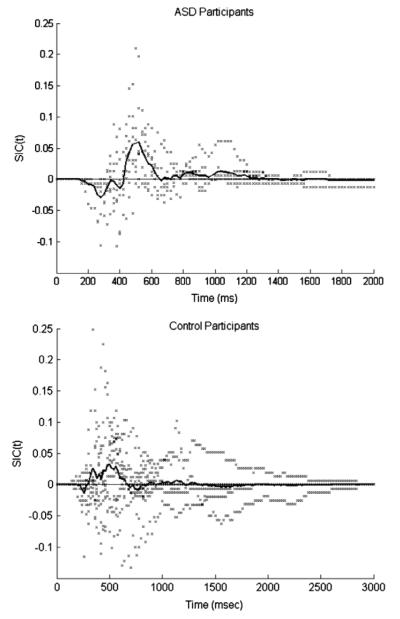
Fig. 8.
Survivor interaction contrast (SIC) functions for the seven ASD participants whose data could be modeled and all control participants. Individual participants are plotted with the points. The solid lines represent the overall SIC for the pooled group data. Most ASD individual SICs and the ASD group SIC show an S-shaped signature, dipping negatively before going positive, with a larger positive area than negative. This signature is characteristic of a coactive processing architecture or facilitatory parallel exhaustive processing. The control group’s SIC is predominantly positive, consistent with parallel minimum-time processing. The individual SICs of the control participants show more variable behaviours, ranging from strictly positive, to S-shaped to all strictly negative, consistent with inhibitory parallel processing. Note that the pooled data line represents the distribution of all participants’ amalgamated data, not the average of the distributions from each participant.