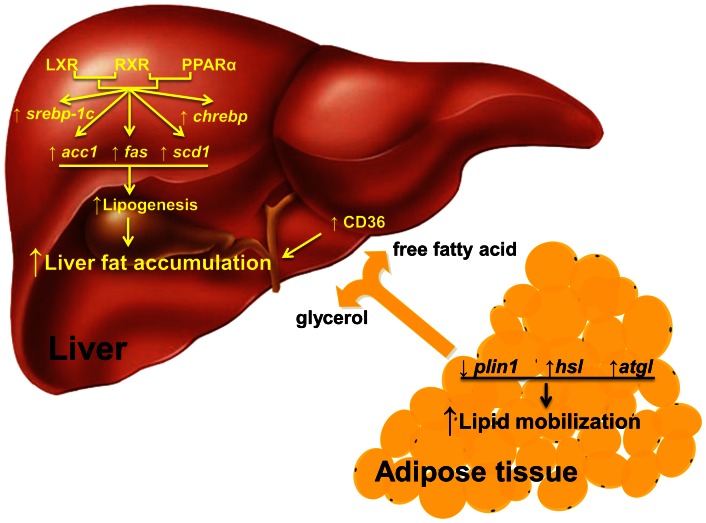
Figure 10. Depicted pathway for the exacerbated hepatic steatosis caused by combined treatment.
Combined treatment activates LXR and PPARα, thereby increasing lipogenesis in the liver via elevating the transcription of srebp-1c, chrebp, acc1, fas and scd1. Meanwhile combined treatment accelerates lipid mobilization in the adipose tissue, thereby releasing more free fatty acids that are transported into hepatocytes by CD36 and further aggravate hepatic steatosis.