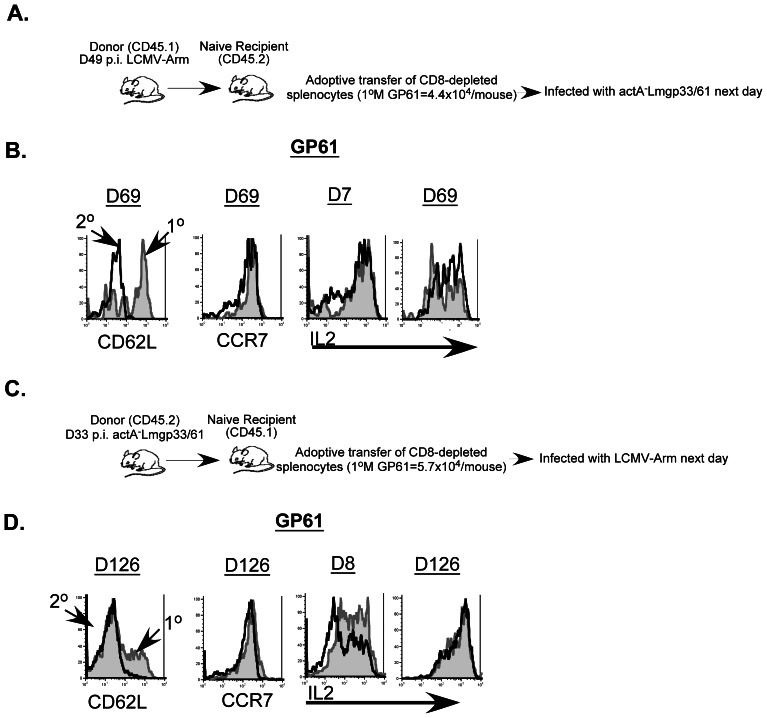
Figure 5. CD62L and IL-2 expression-patterns are selectively altered on memory CD4-T cell subsets following a heterologous-prime-challenge.
(A). Bulk CD4 T cells were purified from spleens of LCMV-infected donor B6 (CD45.1+) mice using negative selection at the indicated time-point after infection and transferred into naïve B6 recipients (CD45.2+) that were challenged the following day with actA−LmGP33/61. (B) Surface expression of CD62L, CCR7 and elaboration of IL-2 was evaluated on primary (endogenous) responders (grey filled histograms) and secondary (transferred) responders (black line). In the converse heterologous prime-challenge experiment, bulk CD4 T cells were purified from spleens of actA−LmGP33/61-infected donor B6 (CD45.2+) mice using negative selection at the indicated time-point after infection and transferred into naïve B6 recipients (CD45.1+) that were challenged the following day with LCMV-Arm (C). (D) Surface expression of CD62L, CCR7 and elaboration of IL-2 was evaluated on primary (endogenous) responders (grey filled histograms) and secondary (transferred) responders (black line).