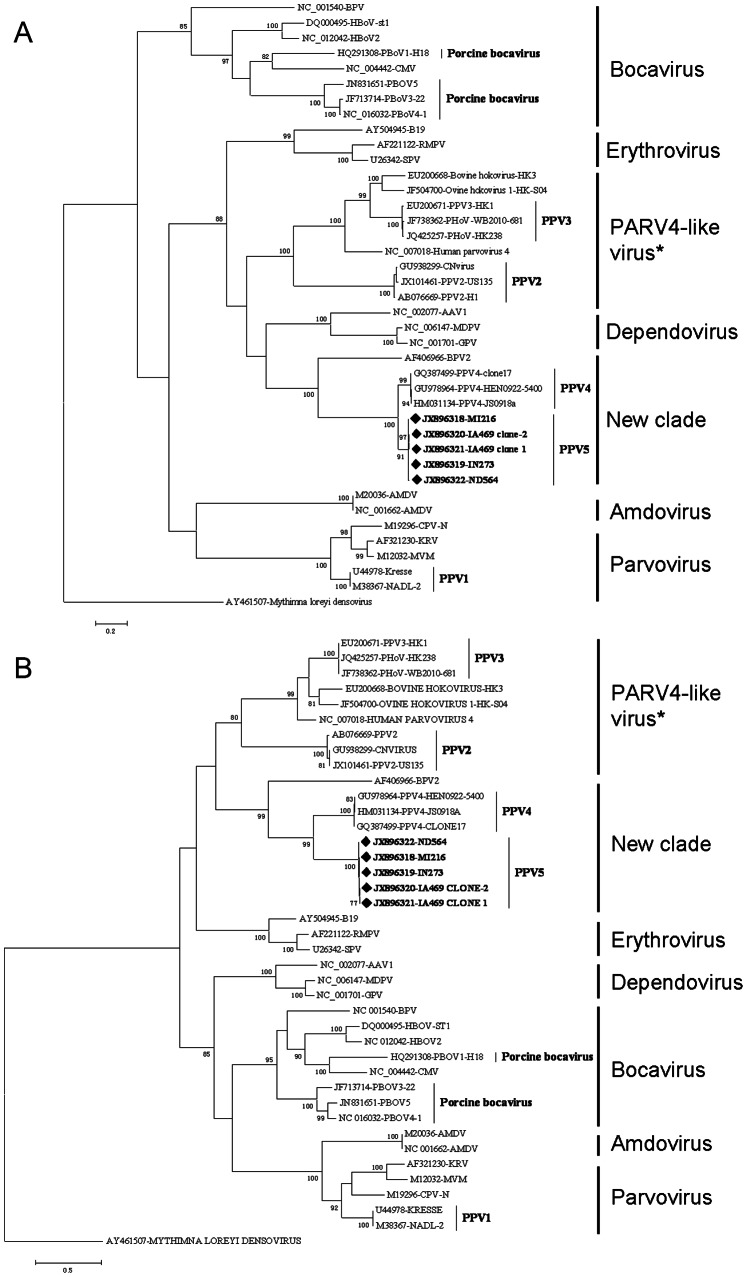
Figure 4. The phylogenetic trees were constructed by using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Poisson correction model, with the amino acid sequences of the nonstructural protein (ORF1, NS1) and the capsid protein (ORF2, VP1).
The percentage of the tree in which the associated sequences clustered together is shown above the branches (only >70% are shown). The trees are drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA5 [34]. The analyses involved 39 sequences of vertebrate parvoviruses with their GenBank accession numbers marked in the tree. PPV5 sequences characterized in the present study are in bold and marked with “♦”. The sequence of Mythimna loreyi densovirus (AY461507) was used as outgroup to root the tree. The asterisk indicates the new genus proposed by ICTV. (A) Tree constructed based on the amino acid sequences of NS1. All positions containing gaps and missing data except ambiguous positions were included. There were a total of 900 positions in the final dataset. (B) Tree constructed based on the amino acid sequences of VP1. All positions containing gaps and missing data except ambiguous positions were included. There were a total of 1,177 positions in the final dataset.