Figure 2. Reduction in the risks for incident cardiac arrhythmias per METhr/d energy expended by walking and running separately relative to the least active walkers.
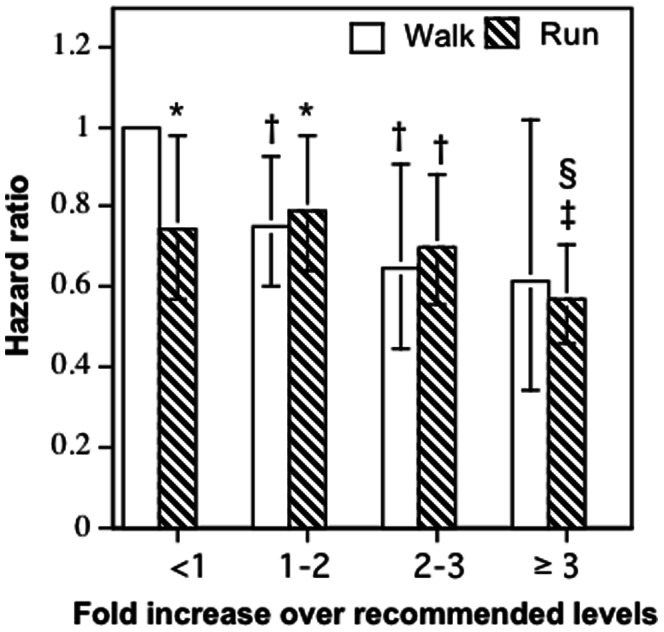
Energy expenditure (X-axis) is categorized in terms of the upper limit of the minimum recommended physical activity levels (750 MET⋅min/wk = 1.8 METhr/d [10], [18]), e.g., 1 to 2-fold higher activity covers from 1.8 to 3.6 METhr/d, etc. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Significant levels relative to the least active walkers coded: * P<0.05; † P<0.01, and ‡ P<0.0001. The superscript § means that the risk for runners who ran ≥3-fold was significantly less than those who ran <1-fold the recommended level (P<0.05).
