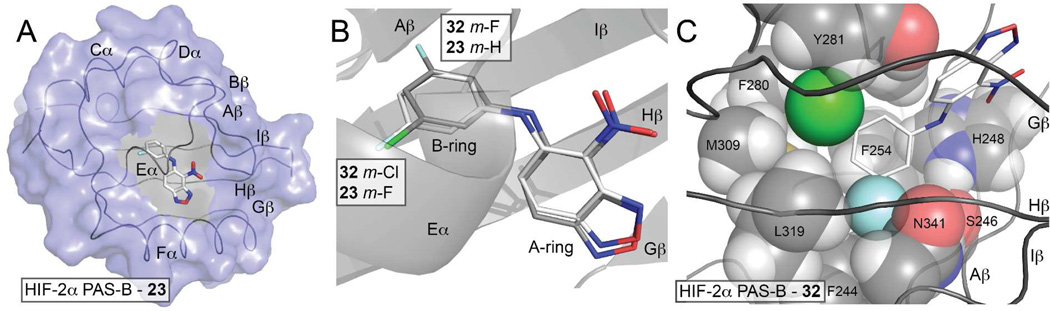
Figure 4.
Binding modes of HIF-2 antagonists. A) The HIF-2 PAS-B* - 23 ternary complex (PDB code: 4GS9) confirms that this inactive HTS-lead analog binds into the HIF-2α PAS-B internal cavity. To better view the internally-bound ligand, secondary structural elements are indicated along the ribbon diagram and the HIF-2α PAS-B surface (blue) has been cut away for residues that separate the binding site from bulk solvent (from this perspective). Although present in these structures, the ARNT PAS-B domain has been omitted for clarity. B) Comparison of the HIF-2 PAS-B complexes with compounds 23 and 32 shows that the mono-substituted m-fluorinated B-ring of 23 flips roughly 180 degrees relative to 32 (PDB code: 4GHI7). C) Close protein - 32 contacts at the m-fluorine site suggests that bound 23 adopts a lower energy bound conformation by placing its single halogen where 32 positions its m-chlorine.