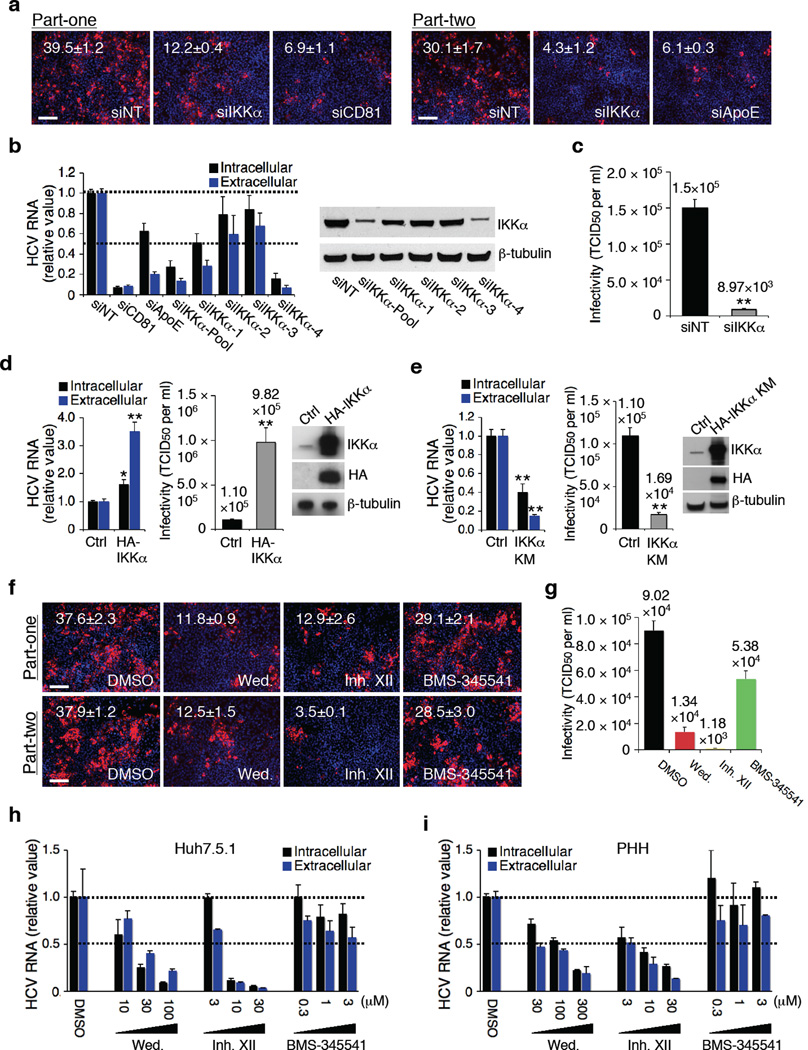
Figure 1.
Role IKKα in HCV infection. (a) Image illustration and quantitative analyses of HCV core staining part-one and part-two. Red: HCV core, blue: cell nuclei. Magnification 20 ×. (b) Efficacies of various IKKα siRNAs in silencing IKKα and restraining HCV RNA production. Values were normalized as relative to nontargeting siRNA (siNT) control. (c) Effect of IKKα depletion on infectious HCV production and secretion, assessed by limiting dilution assay. (d) Effect of over-expression of IKKα on HCV infection. (e) Effect of over-expression of the kinase-defective HA-IKKα KM on HCV infection. (f,g) Effects of wedelolactone (30 µM) and IKK inhibitor XII (10 µM) on HCV production (f) and viral infectivity (g). (h,i) Dose-response effects of wedelolactone and IKK inhibitor XII on HCV RNA production and secretion in Huh7.5.1 cells (h) and PHHs (i). Error bars represent ± s.d. of triplicate experiments. (a,f) Scale bars represent 100 µm.