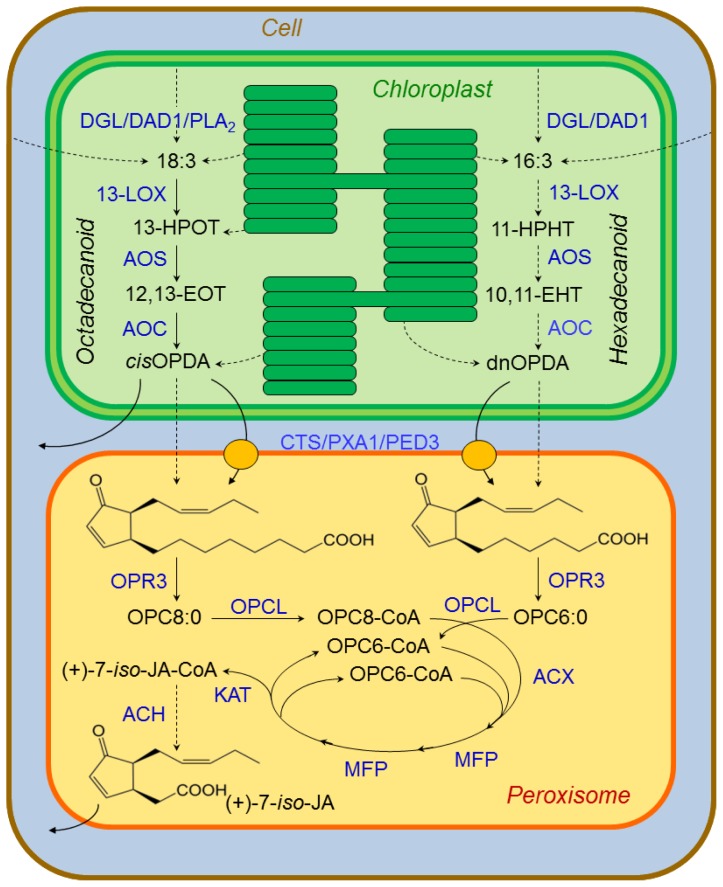
Figure 5.
Biosynthesis of jasmonic acid in the chloroplast and peroxisome. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (18:3 and 16:3) released from the cell, chloroplast and/or thylakoid membrane are precursors for the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid (JA). Within the chloroplast, cis-(+)-12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (cisOPDA) and dinor-OPDA (dnOPDA) are formed via the octa- and hexadecanoid pathways. After transport into the peroxisome, OPDA (dnOPDA) is reduced to OPC8:0 (OPC6:0) and undergoes three (two) cycles of β-oxidation that results in the production of (+)-7-epi-jasmonic acid. The reactions are catalyzed by lipoxygenases (LOX), allene oxide synthase (AOS), allene oxide cyclase (AOC), ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter COMATOSE (CTS/PXA1/PED3), 12-oxophyto-dienoate reductase (OPR3), OPC CoA ligase1 (OPCL), acyl-thioesterase (ACH), 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase [132], acyl-CoA oxidase (ACX) and a multifunctional protein (MFP). Enzymes are shown in blue. Arrows show the well characterized reactions, whereas dashed arrows show steps that are still hypothetical, and for which the corresponding enzymes remain to be identified. (Adapted from [117,133]).