Figure 6.
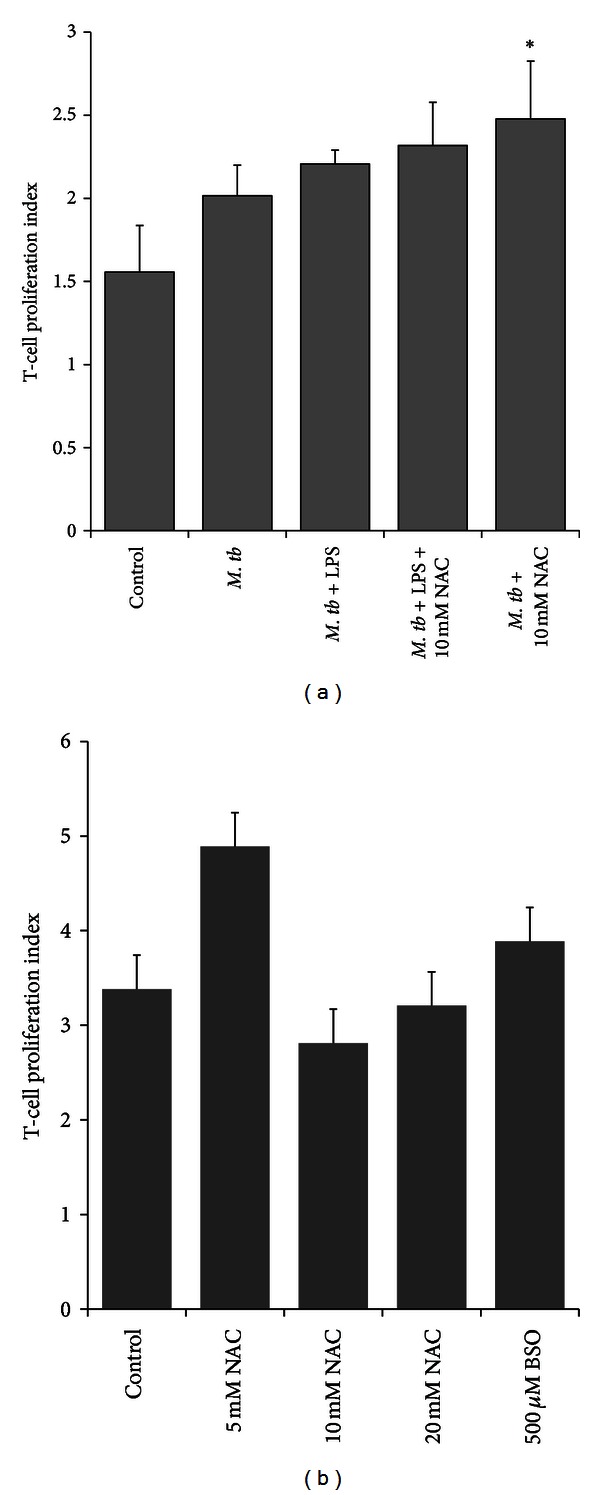
DCs and T cell proliferation assays. (a) Allogeneic T cell proliferation in response to H37Rv-infected, NAC treated DCs. DCs were treated overnight with NAC (10 mM) either alone or in combination with NAC + LPS (1 μg/mL). Following overnight incubation with NAC, DCs were infected with H37Rv, washed, and resuspended in fresh media containing no additives. Allogeneic T cells isolated from PBMCs using a nylon wool column were stained with CFSE (1 μM). Labeled T cells were added to the wells containing infected DCs. Seven days post-incubation, T cells were aspirated and fixed in PFA and analyzed for T cell proliferation using flow cytometry. (b) Proliferation of GSH-enhanced T cells in response to H37Rv-infected DCs. GSH levels in T cells (not DCs) were manipulated by overnight treatment with different concentrations of NAC (5, 10, and 20 mM). Following overnight incubation with NAC, T cells were washed three times with PBS, labeled with CFSE, and then added to the infected DCs to determine the ability of GSH-enhanced T cells to effectively respond to the M. tb-infected DCs and proliferate. Seven days after incubation, T cells were aspirated and fixed in PFA and analyzed for T cell proliferation using flow cytometry.
