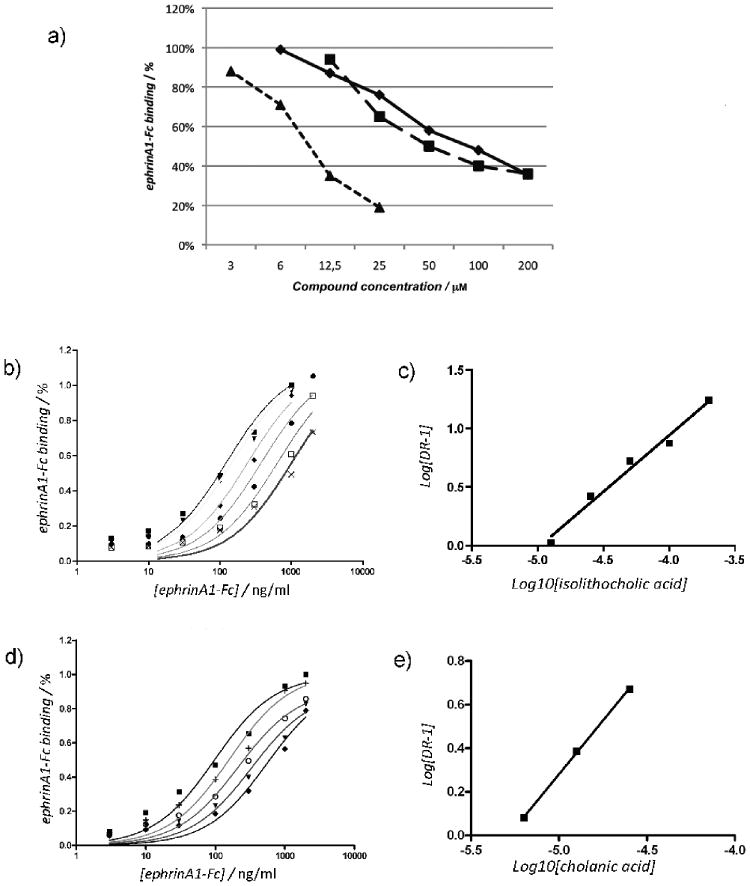
Figure 4.
Isolithocholic and cholanic acid competitively inhibit EphA2-ephrin-A1 binding. a) Lithocholic (●), isolithocholic (■) and cholanic acid (▲) dose-dependently displace ephrin-A1-Fc from the immobilized EphA2-Fc ectodomain. b) and d), binding of ephrin-A1-Fc to immobilized EphA2-Fc in presence of different concentrations of isolithocholic [(0 μM (■), 12.5 μM (▼), 25 μM (◆), 50 μM (●), 100 μM (□), and 200 μM (×)] or cholanic acid [(0 μM (■), 3 μM (+), 6 μM (○),12.5 μM (▼) and 25 μM (◆)] respectively. c) and e). The dissociation constants (KD) from the displacement experiments shown in b) and d) were used to calculate Log (dose-ratio - 1) and to graph the Schild plots for isolithocholic (slope = 0.96 ± 007) or cholanic acid (slope = 0.98 ± 002). pKi values were estimated by the intersection of the interpolated line with the X-axis. The slope of the interpolated line can be related to the nature of the binding. A slope between 0.8 and 1.2 indicates competitive binding, whereas a higher slope suggests non-specific interactions. (Ki = 25 ± 4 μM for isolithocholic acid; Ki = 5.1 ± 1.4 μM for isolithocholic acid).