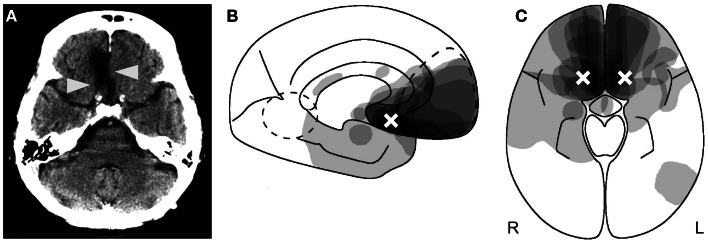
Figure 1.
Anatomy of reality filtering. (A) Typical orbitofrontal lesion causing reality confusion. In this case, the right gyrus rectus is destroyed (arrowheads) following rupture of an aneurysm of the anterior communicating artery. (B,C) Superimposition of the lesions of 14 patients who confused reality for weeks to months. (B) Sagittal cut; (C) axial cut. As indicated by the shades of gray, maximal lesion overlap was in the posterior medial orbitofrontal area. The white crosses indicate the area of peak activity in healthy subjects who performed a similar task as the one on which the reality-confusing patients failed. (B,C) Reproduced from Schnider (2008), with permission.