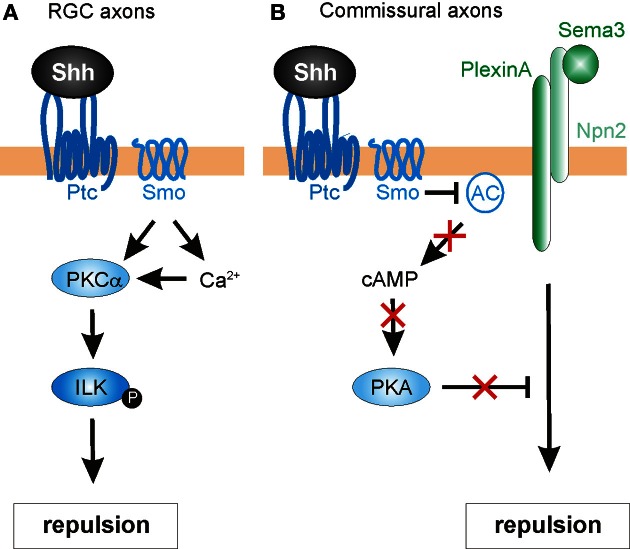
Figure 5.
Intracellular mechanisms mediating Shh-induced repulsive axon guidance. (A) In RGC axons, Shh binding to Ptc promotes the Smo-dependent activation of protein kinase Cα (PKCα), which in turn phosphorylates integrin-linked kinase (ILK). ILK promotes repulsive axon turning. (B) In commissural neurons, Shh acts through Ptc and Smo to block adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity. This lowers cAMP levels and inhibits protein kinase A (PKA) activity. In turn, this confers growth cone sensitivity to class 3 semaphorins (Sema3), by allowing repulsive signaling downstream of a PlexinA-Npn2 complex.