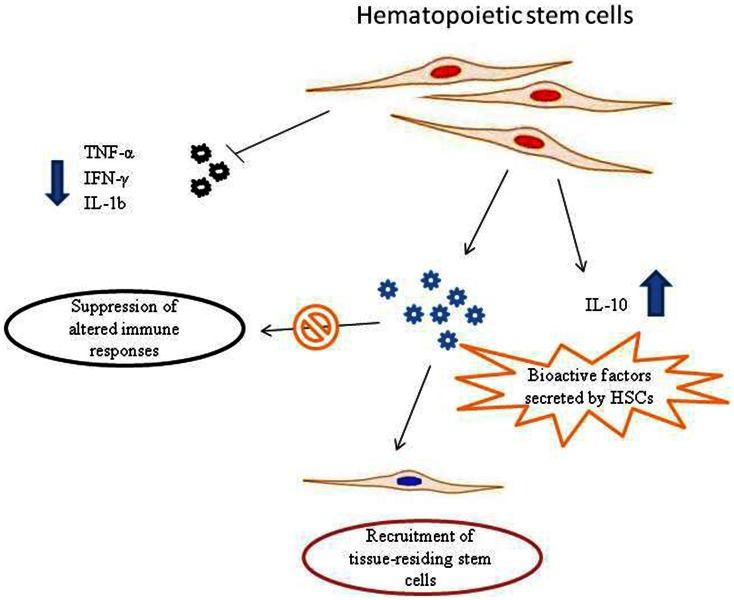
Figure 1.
Possible mechanisms of action of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) therapy. Pro-inflammatory molecules released in ASDs could recruit HSCs to the site of inflammation. HSCs synthesize and release a broad variety of biofactors, including cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. These bioactive molecules secreted from stem cells are able to suppress aberrant immune responses and stimulate recruitment, retention, and activation of tissue-residing stem cells. In addition, HSCs are able to down-regulate the pro-inflammatory TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-1, that are responsible for neuroinflammatory processes in ASDs, as well as to up-regulate the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10.