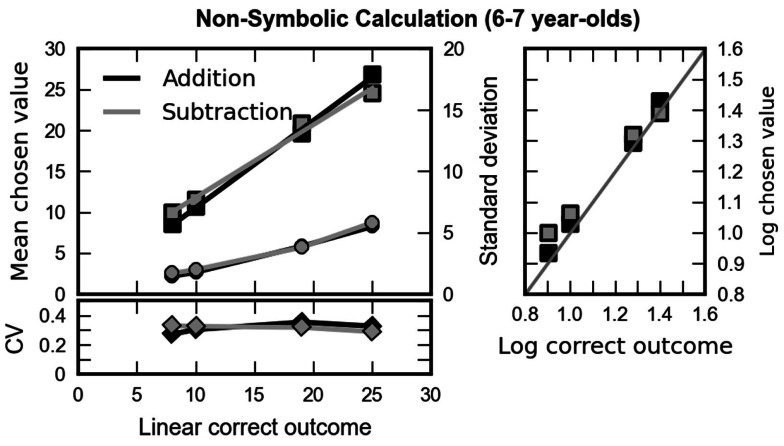
Figure 4.
Left column: mean responses (chosen values, squares) of the children and standard deviations (circles) plotted against the correct outcome for addition (black) and subtraction problems (gray). The lower part depicts the coefficient of variation (CV, diamonds) – that is, the ratio of standard deviation and mean chosen value, plotted against the correct outcome. A constant coefficient of variation indicates that variability of chosen values increased proportionally with mean chosen value. In turn, this can be understood as an instantiation of Weber’s law. Right column: the logarithm of the correct outcome plotted against the logarithm of the mean value chosen by the children for addition (black) and subtraction (gray). The gray line indicates a ratio of 1 – that is, perfect performance.