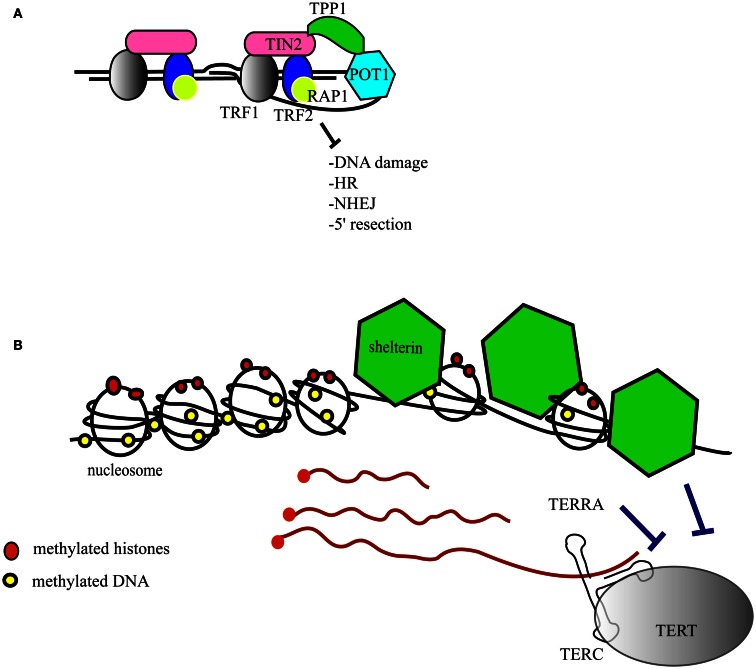
Figure 1.
Structure of the telomeres. (A) The telomere folds into a telomeric loop (t-loop) and binds the six-protein subunit complex shelterin. TRF1 (in gray) and TRF2 (in blue) bind double-stranded telomeric DNA. POT1 (in light blue) binds to single-stranded telomeric DNA. RAP1 (in yellow) is recruited to the telomere by an interaction with TRF2. TIN2 (in pink) serves as a scaffold to recruit TRF1, TRF2, and TPP1 (in green), which in turn interacts with POT1. The main functions of shelterin are listed in the figure and further details are given in the text. HR, homologous recombination; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining. (B) Epigenetic marks at the telomere (red dots represent histone methylation and yellow dots represent DNA methylation). The shelterin complex (green) regulates nucleosome spacing. The telomeres are transcribed into TERRAs (red strings) that inhibit telomerase catalytic activity, and shelterin inhibits telomerase access. TERC, the RNA component of telomerase; TERT, the catalytic subunit of telomerase.