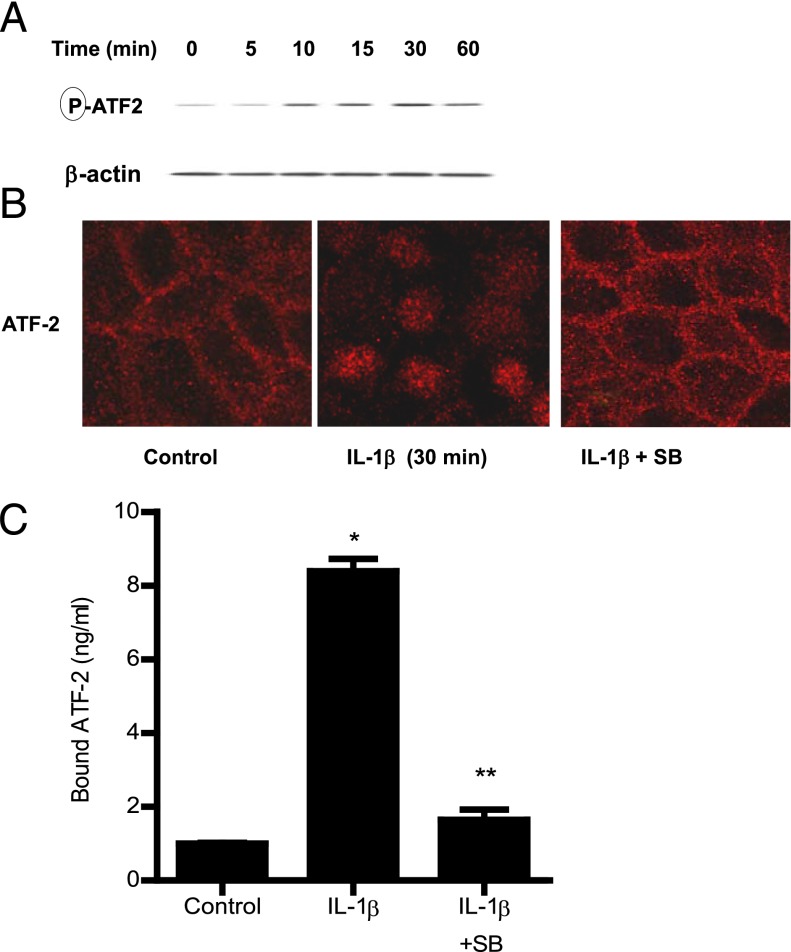
FIGURE 3.
Effect of IL-1β on ATF-2 activation. (A) IL-1β (10 ng/ml) caused a time-dependent increase in ATF-2 phosphorylation as assessed by Western blot analysis (n = 3). (B) IL-1β treatment resulted in ATF-2 cytoplasmic-to-nuclear translocation as determined by immunofluorescent Ab labeling as described in Materials and Methods (30-min experimental period) (n = 3). Pretreatment with p38 kinase inhibitor SB-203580 1 h prior to IL-1β treatment prevented the IL-1β–induced ATF-2 nuclear translocation. Original magnification ×40. (C) Pretreatment with p38 kinase inhibitor SB-203580 1 h prior to IL-1β treatment prevented the IL-1β–induced binding of ATF-2 to its binding site on DNA probe as measured by DNA ELISA binding assay (n = 6). *p < 0.001 versus control, **p < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment.