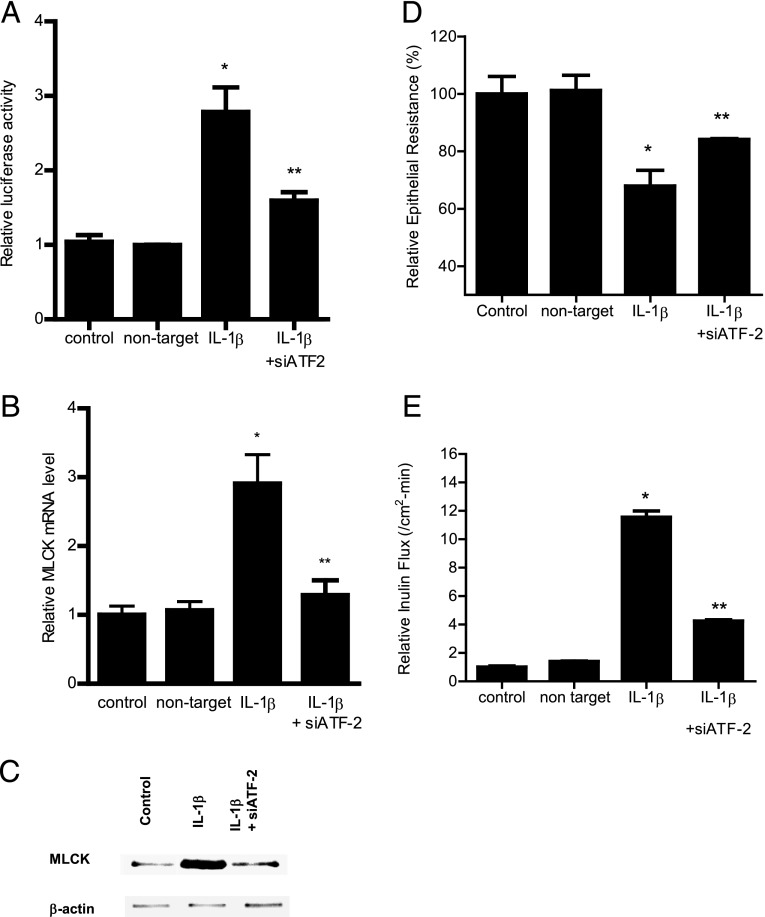
FIGURE 4.
Effect of siRNA-induced ATF-2 knockdown on IL-1β–induced increase in Caco-2 MLCK expression. (A) ATF-2 siRNA transfection significantly prevented the IL-1β–induced increase in Caco-2 MLCK promoter activity as assayed by luciferase assay in the 4-h experimental period (n = 8). *p < 0.001 versus control, **p < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment. (C) ATF-2 siRNA transfection inhibited the IL-1β–induced increase in Caco-2 MLCK mRNA levels in the 6-h experimental period (n = 8). *p < 0.001 versus control, **p < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment. (D) ATF-2 siRNA transfection prevented the IL-1β–induced increase in Caco-2 MLCK protein expression in the 48-h experimental period (n = 3). (E) ATF-2 siRNA transfection prevented the IL-1β–induced drop in Caco-2 TER in the 48-h experimental period (n = 6). *p < 0.001 versus control, **p < 0.001 versus IL-1β treatment. (B) ATF-2 silencing inhibited the IL-1β increase in mucosal-to-serosal inulin flux in the 48-h experimental period (n = 6). *p < 0.0001 versus control, **p < 0.0001 versus IL-1β treatment. Caco-2 monolayers were cotransfected with siRNA ATF-2 for 96 h before IL-1β treatment.