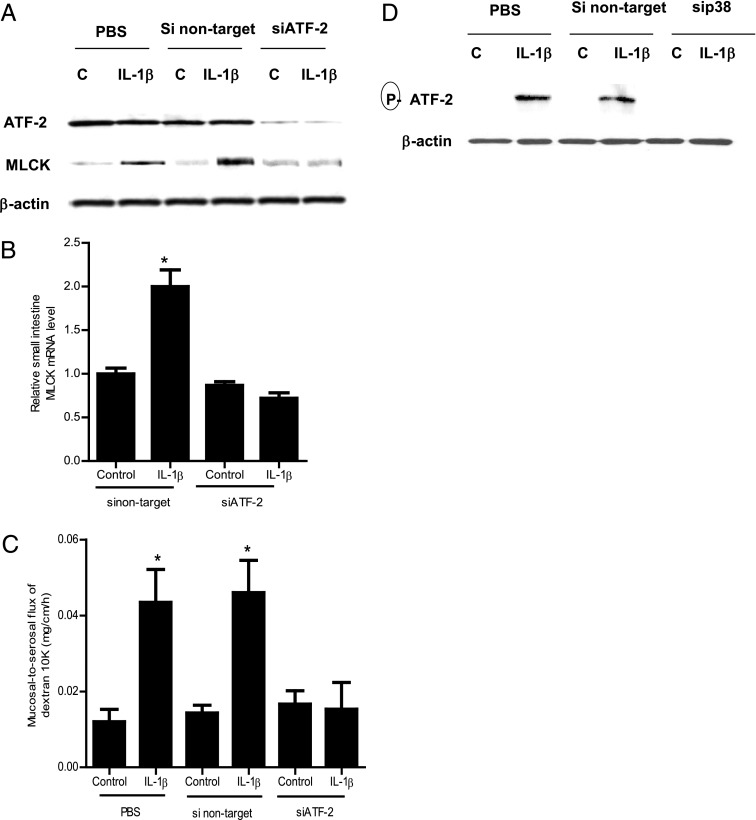
FIGURE 7.
Effect of siRNA-induced ATF-2 knockdown on IL-1β–induced increase in mouse intestinal MLCK expression and mouse intestinal permeability. (A) ATF-2 siRNA transfection resulted in a nearly complete depletion in mouse intestinal ATF-2 protein expression. ATF-2 siRNA transfection prevented the IL-1β–induced increase in mouse intestinal MLCK protein expression in the 24-h experimental period (n = 3). (B) ATF-2 siRNA transfection inhibited the IL-1β–induced increase in mouse MLCK mRNA levels in the 24-h experimental period (n = 3). *p < 0.001 versus control. (C) ATF-2 silencing inhibited the IL-1β increase in mucosal-to-serosal flux of dextran (10 kDa) in the 24-h experimental period (n = 3). *p < 0.0001 versus control. (D) siRNA-induced knockdown of p38 kinase prevented the IL-1β–induced activation (phosphorylation) of ATF-2 in mouse intestinal tissue in the 4-h experimental period (n = 3).