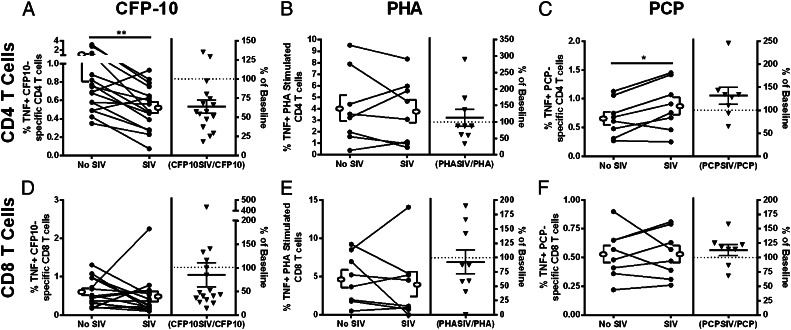
FIGURE 1.
SIV reduces the frequency of TNF-producing CFP10-specific CD4 T cells. PBMCs were stimulated with M. tuberculosis–specific Ags (CFP10; A and D), with PHA (B and E) or Pneumocystis jirovecii kexin (PCP; C and F). TNF expression in CD4 (A–C) and CD8 (D–F) T cells was measured by flow cytometry. SIV caused significant decreases in the frequency of TNF-expressing CFP10-specific CD4 T cells [n = 16 animals; (A)] and increases in P. jirovecii–specific CD4 T cells (n = 8 animals; C). No change was observed in PHA-stimulated CD4 T cells [n = 9 animals; (B)] or CD8 T cells (D–F). Open ellipse and bracket to the left and right of the line graphs represent mean ± SEM. The column on the right side of each graph indicates the percent difference in responses from PBMCs incubated with SIV compared with PBMCs without SIV (triangles; line represents mean ± SEM percentage). The dotted line represents the baseline cytokine response in T cells from PBMCs without SIV. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test was used with significance set at p < 0.05. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.