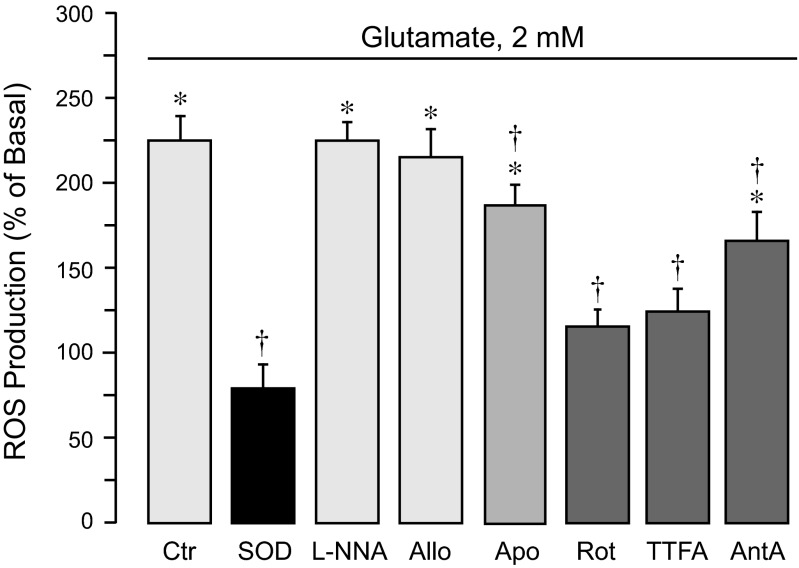
Fig. 1.
Intracellular sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) activated by glutamate in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (CMVEC) from newborn piglets. Confluent quiescent CMVEC were untreated (baseline) or exposed to 2 mM glutamate for 1 h in the absence (Ctr) or presence of ROS inhibitors: superoxide dismutase (SOD from bovine erythrocytes; 1,000 U/ml); a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, NG-nitro-l-arginine (l-NNA; 1 mM); a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, allopurinol (Allo; 50 μM); a NADPH oxidase inhibitor, apocynin (Apo; 0.5 mM); a mitochondrial complex I inhibitor, rotenone (Rot; 1 μM); a complex II inhibitor, thenoyltrifluoroacetone (TTFA; 5 μM); or a complex III inhibitor antimycin A (AntA; 1 μM). ROS production was measured by accumulation of oxidized dihydroethidium (Ox-DHE) fluorescent products and expressed as %baseline values. Data represent the average of 4 experiments. Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05, compared with the basal value. †P < 0.05, compared with glutamate alone.