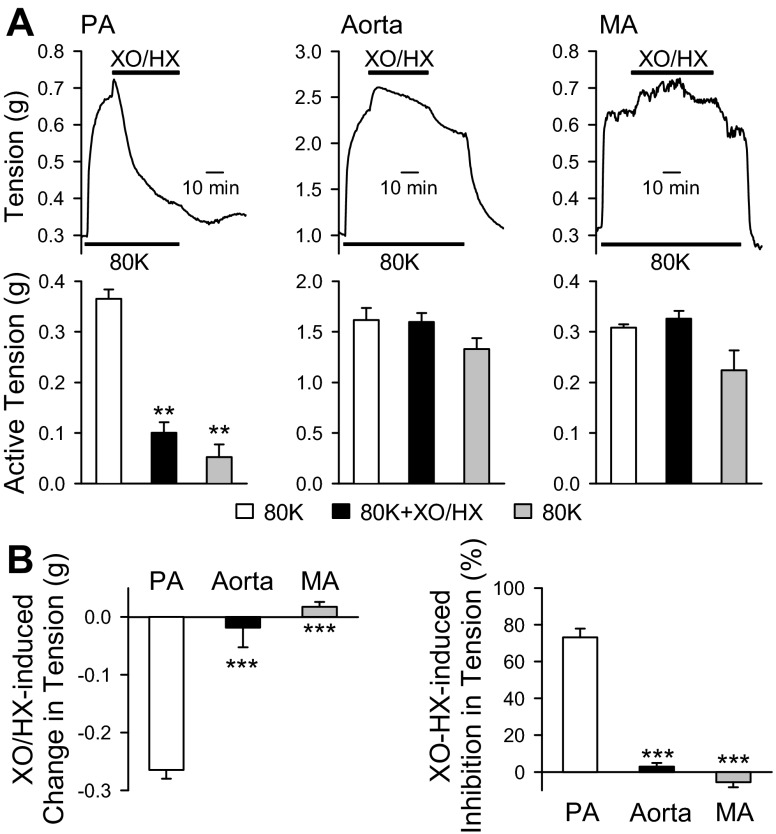
Fig. 6.
ROS produced by XO/HX inhibits 80 mM K+ (80K)-induced contraction in mouse PA but not in aorta and mesenteric artery (MA). A: representative tension traces (top) and summarized data (bottom) showing 80K-mediated active tension in PA (left), aorta (middle), and MA (right) in the absence of presence of XO (0.2 mU) and HX (250 μM). XO/HX was applied to the arterial rings when the 80K-mediated contractions reached plateau. **P < 0.01 vs. open bars (80K). B: bar graph showing the changes in 80K-mediated active tension (actual tension in g, left, and %maximal active tension, right) in PA (open bars), aorta (solid bars), and MA (grey bars). Data are expressed as means ± SE. Arteries were isolated from 4–6 mice. ***P < 0.001 vs. open bars (PA).